- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:22.
Numerous ornamental plants develop considerable root systems over the course of their lives, which grow under garden paths or penetrate cracks in facades. To prevent this, spreading plants should be provided with a root barrier. This is also suitable for plants that spread uncontrollably in the garden.

Why do you need a root barrier in the garden?
A root barrier prevents plants with strong root growth from spreading uncontrollably in the garden. It usually consists of plastic film or metal and is buried at various depths around the plant. Root barriers are particularly necessary for spreading grasses, shrubs and trees.
Purchasing Tips
Flexible root barriers are offered in roll form and usually have a material thickness of two millimeters so that they can withstand root pressure. You can determine the dimensions yourself and cut the films. Plastic is a common material for a root barrier. There are metal alternatives for certain areas of application.
Characteristics of an ideal root barrier:
- resistant to chemicals and solvents
- acid, s alt and alkali resistant
- resistant to mold and microorganisms
- to protect pipes with a waterproof coating
- free from plasticizers and toxins that could get into the soil
Plastic

Root barriers made of plastic are usually used
The material offers the great advantage of flexibility. According to a study by the Weihenstephan University of Applied Sciences, a 70 centimeter wide film provides the best protection against root pressure of most ornamental plants in the garden. Root barriers made of polyethylene or polypropylene are common. The ends of the film are connected to aluminum rails that can be screwed together. Root runners cannot grow through these rails. Many manufacturers offer a 25-year guarantee on material durability for their products (€24.00 on Amazon).
| Polyethylene | Polypropylene | |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation | HDPE | PP |
| Features | particularly high density and resistance | easy handling due to low weight |
| Note | Laying requires more effort | not suitable for bamboo |
Metal root barrier
Since most metals do not have any corrosion protection, they are not suitable for permanent use in the ground. An alternative with an unfavorable price-performance ratio would be stainless steel. However, there are metal root barriers that are specifically designed for lawns. This prevents the lawn from spreading onto paths or growing into the flowerbeds. Galvanized metal rails made of aluminum, stainless steel or steel are used, which are embedded vertically in the ground.
Application of root barrier

Dig the planting hole and line the walls completely. Make sure that the film lies vertically. Slight slopes cause the roots to be directed upwards. Cut the foil so that the ends overlap by ten to 20 centimeters. The plants are then inserted and the hole is filled with topsoil. The overlaps must not be pulled apart. You can also close the films with butyl adhesive tape or aluminum rails.
How deep is the root barrier laid?
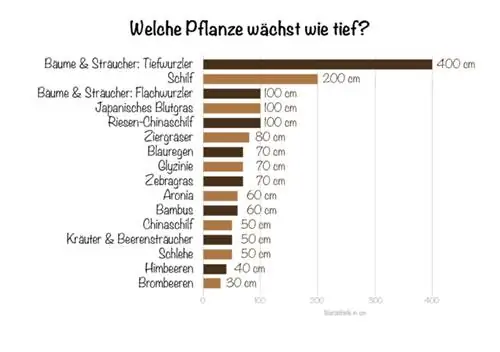
The depth depends on the respective plant species. A 70 centimeter wide film is usually sufficient to suppress the development of runners on most plants. Many strong-growing herbs and shallow-rooted berry bushes conquer depths of between 20 and 50 centimeters with their roots. Depending on the species, impressive ornamental grasses are restricted with a root barrier that extends 60 to 80 centimeters deep into the ground.
Alternatives for root barriers
In numerous hardware stores you will find a wide selection of high-quality branded products and inexpensive own-brand alternatives. For smaller plants, old pots or leftover materials are usually sufficient and you can use them to make root barriers yourself.
| Width | Material | Price per square meter | Providers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gardol root barrier | 70cm | PP | 11, 40 euros | Bauhaus |
| Root barrier FloraSelf | 65 cm | Synthetic fiber with one-sided HDPE coating | 8, 79 euros | Hornbach |
| Root Barrier Premium | 70cm | High-tech material | 13, 33 euros | Obi |
| Dehner root barrier | 70cm | PP | 12.85 Euro | Dehner |
| B1 root barrier | 60cm | Hard plastic | 7, 14 euros | Toom |
Recycle containers and leftover materials
If they are small perennials that spread easily, you can place the root ball in a used mortar bucket and sink it into the ground. You should not use containers made of untreated metal as they will rust due to moisture in the soil.
Many ornamental grasses or sea buckthorn can be planted with conventional roofing foil. The roots of the fast-growing raspberries can be contained with fleece, which is laid to a depth of 40 centimeters. You should make sure that the ends of the material are connected to each other.
Roof foil, garden fleece or pots can be used as a root barrier for some plants.
Pimpled track as a root barrier?
The insulation layer for basement rooms is suitable as a root barrier if the material offers the same properties as conventional barrier film and the dimensions are correct. The most common Gutta studded sheet 'Star' has a material thickness of eight millimeters and is between 50 and 100 centimeters wide. It is made of durable HDPE and, with an average price of 1.80 euros per linear meter, is cheaper than a root barrier.
Which plants restrict with root barriers?
Every plant has different propagation strategies and competitive strengths. Weak species invest their energy in developing flowers and seeds, so they do not pose a problem. Strong herbs, grasses and shrubs conquer large areas in a short time by developing underground runners.
Tip
If you plant herbs such as mint or groundweed in the garden, you should also think about a root barrier here. A large plastic pot sunk into the ground is sufficient.
Grasses

Miscanthus should definitely be planted with a root barrier
Sweet grasses include annual as well as perennial and perennial species, numerous plants of which are planted in the garden as ornamental grasses. Their growth can be broadly divided into two categories. Grasses that form dense or loose clumps are usually loyal to their location and do not grow uncontrollably in the bed. The lawn-like growth habit results from runners that creep on the surface of the earth or are formed underground by the roots. Such species require a rhizome barrier:
- Miscanthus Eulalia (Miscanthus sinensis 'Gracillimus') forms roots at depths between 30 and 40 centimeters
- Miscanthus (Miscanthus sinensis) develops roots about 50 centimeters deep
- Zebra grass roots (Miscanthus sinensis 'Zebrinus') reach 50 to 70 centimeters into the soil
- Japanese blood grass (Imperata cylindrica) has roots 60 to 100 centimeters deep
- Giant miscanthus (Miscanthus × giganteus) grows up to 100 centimeters deep
- Reed (Phragmites australis) can develop roots up to two meters deep
Background
How bamboo grows
Bamboo is a subfamily of sweet grasses, whose species form two different rhizome bodies. The first growth form is characterized by short and thick rhizomes. They develop more or less compact clumps that grow separately from each other.
Long and thin rhizome bodies are characteristic of the second growth form. Such types of bamboo grow more openly, so that the stalks are evenly distributed over a wide area. They are considered to spread easily, which is why a root barrier for such bamboo species at a depth of 60 centimeters makes sense.
Trees and bushes
Over the course of its life, a tree develops strong roots that can cause damage to buildings or pavement slabs. How deep the roots reach into the ground depends on the species. Deep-rooted plants reach a root depth of between two and four meters, while shallow-rooted plants develop their roots extensively in the top layers of the soil. Many of these trees require a root barrier because they spread via underground runners.
Tip
Wisteria is a climbing plant that has deep and shallow roots at the same time in search of water. Therefore, a root barrier for wisteria at a depth of 70 centimeters makes sense.
Ornamental shrubs
For most shrubs, root barriers with a thickness of three to four millimeters and a height of between 45 and 50 centimeters are sufficient. Hydrangeas, ranunculus bushes and magnolias are particularly prone to spreading and should be contained with a four to ten millimeter thick barrier film depending on their root strength.
How deep root barriers must be:
- Thuja: 70 to 80 centimeters
- Willow: depending on the species between 30 and 50 centimeters
- Rosa rugosa: 60 to 70 centimeters
The vinegar tree is a good example of shallow-rooted trees. On sandy and nutrient-poor soils, the species grows within a radius of ten meters around the trunk and forms vigorous thickets there. Root barriers with a thickness of ten to 15 millimeters are recommended.
Fruit bushes

Blackberries and raspberries should be planted with a root barrier
Many fruit bushes are known for their ability to spread and take up large areas within a very short period of time. It is not uncommon for the trees to spread over a radius of more than two meters and suppress any plant growth in this area. This growth is typical for shrubs from the rose family:
- wild blackberries require root barriers at a depth of up to 30 centimeters
- similar dimensions for varieties such as the blackberry 'Navaho'
- Root barriers for raspberries should be 40 centimeters deep
- Blackthorn is planted with a 50 centimeter deep root barrier
- Aronia root barrier should reach 60 centimeters deep into the ground
When are root barriers unnecessary?
In contrast to its namesake, buddleia does not need any root barriers because the shallow-rooted shrub does not form any underground runners. Syringa vulgaris reproduces via root suckers, which can become annoying in certain situations. Therefore, a root barrier for lilacs makes sense.
Plants that survive without root barriers:
- Pampas grass (Cortaderia selloana) forms attractive clumps
- Miscanthus varieties of the variety 'condensatus' usually grow like clumps
- Sacred bamboo does not develop runners
Frequently asked questions
What is a root barrier?
A root barrier prevents a plant from spreading uncontrollably via underground runners in the garden. Durable films are usually used to prevent roots from growing into unwanted areas. The term rhizome barrier is used synonymously. Such root barriers are available at Bauhaus, Hornbach or similar hardware stores.
What is the difference between root barrier and root guidance?
Root barriers are smooth films that cause the so-called flower pot effect on trees. The flat-growing roots spread left-handed and circular on the smooth-walled barrier. Because the tree loses stability as it grows taller, root guidance was developed. Such systems contain vertical ribs that guide the roots into the depths. Once they have reached the lower edge of the barrier, they continue to grow in the natural direction of their growth.
Is a root barrier necessary?
Whether you should integrate a root barrier into the soil depends on the plant in question. A barrier film is unnecessary for species that grow in clumps, as they do not spread via underground runners. Ornamental grasses and herbs that grow over a large area or berry bushes that tend to spread should be equipped with a root barrier unless uncontrolled growth is desired. For smaller plants, you can use alternatives such as roofing foil, or place the plants in a durable plant pot and sink it into the ground.
Does the fig tree need a root barrier?
The real fig is one of the heartroot plants, whose root system is wider than the crown and develops a hemispherical shape. It is usually not necessary to provide the tree with a root barrier. The root system needs space to develop well. Since figs in Germany are preferably planted in protected locations or grown as a trellis on the house wall, a root barrier makes sense to protect the foundation.
Can I plant bamboo without a root barrier?
Whether your bamboo needs a root barrier depends on the species. There are clumpy growing representatives that do not need any root barriers. Ornamental grasses that grow over a wide area tend to spread uncontrollably and should be restricted with an underground barrier. If you plant bamboo, a root barrier with a width of 60 centimeters makes sense.
- a bamboo plant gets a root barrier with a diameter of 150 to 200 centimeters
- Top edge of the barrier should protrude about five centimeters from the ground
- Film is laid so that the diameter at the bottom is smaller than at the top
Can I install a root barrier later?
It is possible to subsequently integrate a root barrier into the garden, but it is not recommended. Strongly growing plants such as bamboo develop an extensive root system and can also sprout new ones from separated rhizome pieces. Dig a trench around the plant that is larger in diameter than the root ball. During this work you will come across the underground shoots, which you will have to cut with a spade and pull out of the ground.






