- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-24 06:09.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:19.
Carpet beetles are among the most feared pests because they don't just cause feelings of disgust. Their feeding activity destroys clothing and larvae have the potential to be harmful to he alth. Before control measures are initiated, the species should be precisely identified. This makes success likely.

Carpet beetle larva under the magnifying glass
Carpet beetles or figwort flower beetles hide where the vacuum cleaner can't reach. They prefer hiding places in wardrobes or nesting in laundry baskets, under beds or between the cushions of sofas. The larvae find optimal places to retreat in carpet fibers or clothing items such as furs and skins. They can appear in lined shoes or cause unpleasant surprises when a long-unused handbag is taken out of the closet. Animal beds and bird cages are also popular hiding places.
Are carpet beetle larvae useful?

Carpet beetle larvae eat leftover animal food
Larvae perform important tasks in nature because they can digest keratin and thus decompose animal remains. Their diet includes skin, fur, feathers or horn. If you find remains of molt, larvae or a nest of eggs under the bed or in upholstered furniture, you should take a closer look. Such hiding places are ideal places to lay eggs, whose appearance has few characteristic features.
Where larvae feel comfortable
A female only lays eggs once per year. She chooses suitable places to lay her eggs that provide food for the larvae. Dust, hair and dander collect under the mattress. Light rarely falls into these dark niches, so carpet beetle larvae feel particularly comfortable here.
Under these optimal development conditions, they can feed, molt and pupate undisturbed. During larval development, molting occurs several times, which is why you can find many molting remains in the typical hiding places in the event of an infestation. The infestation is usually only noticed late.
Do I have carpet beetle larvae in my bed?
The carpet beetle lays whitish eggs that reach a size of 0.7 x 0.3 millimeters. Their shape is variable. Lobe-like projections located at the end of the eggs are typical. Adult carpet beetles are easy to recognize, although the larvae of the introduced Australian carpet beetle differ from those of the figwort flower beetle in body size and color.
Typical appearance of a carpet beetle larva:
- Body is conical at the end
- Hull decorated with tufts of longer arrow hair
- Brownroot flower beetle twelve to 15 millimeters long, golden yellow in color
- Australian carpet beetle up to six millimeters long, brownish and yellowish and white underneath

Larvae but not beetles?
When the larvae pupate depends on the temperature and food availability. They can enter the pupal stage as early as six months or as late as three years. As soon as the beetles hatch, they swarm out and find their way into nature. Due to this variable development, it is more common for you to find many larvae but no beetles.
Different food
Adult carpet beetles feed on pollen and nectar. They have specialized in white-flowering plants and therefore prefer hawthorn, mountain ash or umbelliferous plants. The insects usually cannot find suitable food in apartments, so newly hatched beetles quickly go out into nature in search of food. The larvae, on the other hand, can be found wherever there is food rich in keratin and chitin. Unlike many material pests, carpet beetles do not leave behind droppings that reveal their activity.
Larval food in apartments:
- dried insects
- Dandruff and hair
- Bird feathers or down
- Textiles and wool
- dried plant parts
- Pet food
Where do carpet beetles come from?
The insects occur in environments rich in herbs and bushes that provide sufficient food. They are often found in pigeon houses or bird nests, as the larvae have a good chance of survival here. Carpet beetles are cultural followers and live predominantly in human environments.
Living space apartment
Adult beetles are attracted to light and enter the apartment in the evening through open windows and doors. When they want to leave the house during the day, they are attracted to daylight and gather on window panes. Their larvae avoid the light and retreat into dark hiding places such as cracks in floorboards.
Detecting malicious images
Wool, fur, carpets or hides can be damaged by the feeding activity of carpet beetles. Larvae can be found on all clothing that has been freshly washed or contaminated with leftover food and sweat. Infested textiles show specific signs of feeding that can be confused with the activity of clothes moths or fur beetles.
The holes of both pests are irregular. In contrast to carpet beetles, clothes moths leave behind typical webs. In comparison to the fur beetle, whose larvae feed on the hair roots of fur textiles, the larvae of the figwort flower beetle mainly feed on the tips of the hair.
Are carpet beetles dangerous?
Many people report numerous bites that they attribute to carpet beetles. The insects actually cause he alth problems. Adult beetles and their larvae must be considered separately because not every stage of development is dangerous to he alth.
Can carpet beetles cause bites?

Adult carpet beetles are pure herbivores
Adult carpet beetles feed exclusively on nectar and pollen, which is why they are classified as harmless to humans. Carpet beetle larvae can bite through cardboard or paper. However, they are unable to damage human skin with their mouthparts. They neither cause a bite nor are they responsible for typical stings.
Larvae can be harmful to humans
A rash is often confused with a sting or bite. Redness and hives are the result of an allergy caused by the long hair of the larvae. Skin rashes that resemble bite wounds arise from direct contact, for example when you put on a wool sweater in which larvae have nested. Proteins found in the hair and feces of the larvae can also trigger allergic reactions when inhaled.
How can I get rid of carpet beetles?
Once you have clearly identified the pests, you can take control measures. While you should pay attention to the larvae and eggs of the figwort flower beetle, all development stages of the Australian carpet beetle must be removed. This species lives exclusively in buildings and, unlike its relatives, produces several generations in one year.
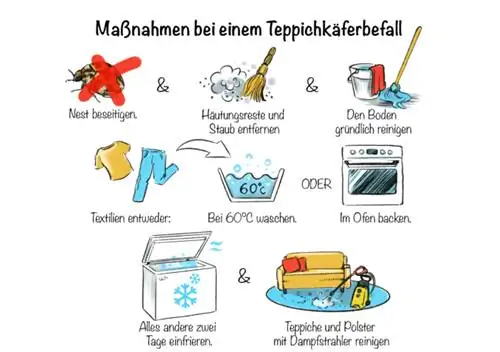
What to do about carpet beetles?
- Find a “nest” and remove accumulations of larvae
- Remove skin residue and dust
- clean thoroughly and let niches dry
- wash suitable textiles at 60 degrees or bake in the oven
- freeze everything else for at least two days
- Clean carpets and upholstery with a steam jet
You usually find remains of the molt or live larvae by chance, so not every hiding place can be found. Thoroughness is therefore the top priority when combating it. You should take several measures to completely eliminate beetles, larvae and eggs.
Combating carpet beetles: Trap as the first measure
If you want to get rid of carpet beetles, you should first determine the severity of the infestation. A trap that attracts the adult beetles is suitable for this purpose. In both sticky traps and pheromone traps, the insects stick to a glued surface and die. Pheromone traps are species-specific and only attract male beetles. Sticky traps without sexual attractants attract both female and male carpet beetles.
| Pheromone trap | Glue traps | |
|---|---|---|
| Placement | on the windowsill | near the infestation sites |
| Control | if necessary | daily |
| Benefit | for eliminating adult beetles | to detect an infestation |
| Ingredients | Sexual attractant | Flavors and glue |
| Advantage | do not attract other insects | cheaper option |
From the captured individuals you can estimate how many larvae can develop. A female figwort flower beetle lays up to 20 eggs. In the Australian carpet beetle, the number of eggs and reproduction rate vary depending on the temperature.
Remove with vacuum cleaner

Regular vacuuming prevents infestation and removes any larvae and their food
Suctioning all niches is the first step to remove eggs and larvae as well as the remains of their molt. Thoroughness is extremely important because the beetle larvae can be in a variety of places in the home. They retreat into picture frames or live between inaccessible shelves. To vacuum such cracks, use the thinnest possible upholstery nozzle. Then dispose of the vacuum cleaner bag in the garbage can so that the larvae do not crawl into the apartment again.
Get rid of larvae in the bed
Remove the bed and wash the covers. Take the mattress out of the bed box and place it on the balcony or terrace to ventilate. By knocking them out, you deprive the larvae of important food sources such as hair and skin flakes. The mattress dries well in the sun, so that the living conditions for the beetle larvae worsen.
You should avoid using poison in the bedroom. Instead, place lavender sachets or cedar wood blocks in the bed box, as the smell repels harmful insects such as carpet beetles.
Anyone who finds larvae in the bed should identify the species exactly. Otherwise, most control attempts end unsuccessfully.
Silicate powder or diatom flour
Some organisms develop skeletons with a pebble-like structure. Diatomaceous earth, which acts like silicate powder, is made from the shells of fossil diatoms or diatoms. Fossil plankton is an effective way to kill carpet beetles and their larvae. Scatter it into all hiding places and niches so that the organisms are pollinated directly. The crystalline structure of the particles destroys the protective wax layer and absorbs liquid, so that the creatures dry out after a short time. Diatomaceous earth is harmless to humans.
Does baking soda help against carpet beetles?
The raising agent is one of the popular remedies that destroys pests naturally. In fact, the powder has a deadly effect. However, you must dust larvae and beetles thickly with baking soda. The fine particles primarily block the insects' breathing openings, causing them to slowly suffocate. If the beetles do not come into contact with the agent, there will be no effect.
Excursus
This is how beetles breathe
The insects' shells are dotted with numerous tiny holes that ensure the oxygen supply. The gas flows through the openings into a network of tubes called tracheas. These invaginations are lined on the inside by a thin layer of chitin and are stabilized by ring-shaped thickenings. On the one hand, body movements ensure breathing, but the different concentrations of gases also influence the exchange. In this way, the used air is exhaled while fresh oxygen reaches the organs.
Deter with essential oils
The aromas of various plants act as so-called repellents. They deter many material pests such as carpet beetles. Such natural fragrances are harmless to most people, but can have a disturbing effect on the well-being of sensitive people. Test beforehand which aromas you find pleasant. Since essential oils are volatile and quickly lose their effect, you should replace the substances regularly and after three months at the latest.
- Lavender: place dried flowers in bags or use lavender oil
- Coniferous trees: roughen fresh cedar wood with sandpaper or vaporize incense sticks with the scent of cedar wood
- Deciduous trees: Drizzle Australian tea tree or neem tree oils into bowls
- Patchouli: distribute leaves, granules or oil
Neemoil
Neem oil is a natural insecticide that negatively affects the development cycle of insects. If the beetles come into contact with the neurotoxin, they stop feeding. They suffer from reduced vitality and can no longer reproduce.
Pyrethrum
If the infestation is particularly severe, only insecticides usually help. Pyrehtrum is a natural active ingredient obtained from chrysanthemums. When exposed to light, the substance decomposes within a short time and the effect wears off. Therefore, products to combat pests are enriched with a chemical enhancer. Products containing piperonyl butoxide (PBO for short) are not natural products and can have a negative impact on he alth.
Effect on insects:
- Impairment of the nervous system
- Blocking sodium channels in the nerve membranes
- Nerve cells cannot rebuild their resting potential
Tip
Many wool carpets have been treated with pyrethroids to protect them from moths and beetles. This pretreatment is a criterion of the wool seal, which is awarded for carpets.
Species and relatives

The museum beetle looks quite similar to the carpet beetle
The common carpet and museum beetles belong to the genus Anthenus. They are a few millimeters long and have a rounded shape. The material pests are often reminiscent of ladybirds. Their antennae have a characteristic feature that allows carpet beetles to be clearly identified. They end in a small club, which is slightly thicker in males than in females.
| scientific | colloquial | Appearance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brownroot flower beetle | Anthrenus scrophulariae | carpet beetle | in nature and in buildings |
| Australian carpet beetle | Anthrenocerus australis | carpet beetle | are limited to indoor living in Europe |
| Eyeweed flower beetle | Anthrenus verbasci | Museum Beetle | almost exclusively in human surroundings |
| Cabinet Beetle | Anthrenus museorum | Museum Beetle | common with the carpet beetle |
Color variety
Most species are characterized by a striking pattern that appears on the dark-colored cover wings. These are covered by brown, red, white or gray scales that wear away with age. In older beetles, the abrasion is sometimes so advanced that the body completely shines in the black base color.
Characteristic drawings:
- Brownroot flower beetle: almost continuous red band, three hints of light cross bands
- Australian carpet beetle: white spots and light zigzag bands, partially broken up into spots
- Eyeweed flower beetle: three light wavy crossbars, the spaces in between have brown scales
- Cabinet beetle: black, white and brown-yellow scales in variable patterns
Danger of confusion: fur beetle
Species of a related genus cause similar damage. Fur beetles are also among the bacon beetles, which, as cultural followers, prefer to settle close to humans. Typical of these species is the fine body hair, which is how the insects got their German name.
Unlike carpet beetles, fur beetles do not have noticeable scales. Both the brown and common fur beetles have a dark coloration that varies between brown and black. This means they can easily be confused with carpet beetles, which appear dark due to the loss of their colored scales.
What you need to know about carpet beetles
In early spring, carpet beetles suddenly appear out of nowhere. They crawl out of their wintering quarters and swarm out in search of food. They fly in the direction of daylight to find nectar and pollen. In spring, carpet beetles can be observed in large numbers on various plants such as chervil, wild carrots or spar bushes.
Mating
After the beetles hatch, they go looking for food. They prefer to fly to white flowers, where ripening occurs. Pollen and nectar are consumed in large quantities to generate energy. Females and males meet at the flowers so that mating occurs.
Egg laying
The females consciously choose darker places to lay their eggs and increasingly avoid the brightness. In the evening you enter apartments through open windows and doors. Light sources attract additional carpet beetles from outside. The majority of eggs are laid between May and June. As a rule, a female lays up to 20 eggs directly into the breeding substrate. The clutch can also contain around 40 eggs. This makes carpet beetles less productive than other species.
Development

The larval stage can last up to four months
At room temperatures, the first larvae hatch after about two weeks. A larva goes through five to six stages of molt before pupating. The higher the temperatures, the faster the eggs develop into adult beetles. At 27 degrees Celsius, complete development takes between three and four months. If the conditions are unfavorable, the development cycle can extend to several years.
- some of the larvae develop into beetles in the same year
- many beetles overwinter in the pupal shell and do not emerge until the following spring
- Larvae often overwinter in unheated rooms
Tip
Remnants of molt can also be assigned to specific species or genera. If the larva leaves a shell with a conical shape and tufts of hair, it is a speck beetle.
Frequently asked questions
How do I recognize carpet beetles?
The appearance of the adults is characterized by an oval body shape, which makes them similar to ladybugs. All Anthrenus species have this characteristic. Carpet beetles reach a size of between three and five millimeters.
The basic color is black, with young beetles being completely covered by scales of a different color. These create an almost continuous red band along the elytra seam. Typical are three suggested light-colored transverse bands that run across the cover wings. Additional reddish scales may be present on the sides. As they age, the scales rub off, making the beetles darker.
Distinguishing feature Pronotum:
- light red on the sides and dark in the middle
- red coloring at the seam to the cover wings
- In addition to this red variant, there are yellow variants
Why can carpet beetle larvae digest keratin?
Keratin is a protein that forms hair or feathers. It is insoluble in water and consists of numerous disulfide bridges that only a few species can break down. These specialists include not only carpet beetle larvae but also clothes moths. The larvae of the figwort flower beetle can only feed on feathers and hair because special microorganisms live in their intestinal appendages. These are able to synthesize essential substances and thereby promote the digestion of keratin.
How quickly do carpet beetles develop?
Variing amounts of time can pass from the egg to the adult beetle. How quickly the larvae go through their individual development stages depends largely on the temperature. They go through several stages, between which they shed their skin. The number of larval stages also varies between six and twelve. At normal room temperatures, the entire development takes about 3.5 months. If the conditions are unfavorable, it can take up to 24 months and rarely three years.
How long does a carpet beetle live?
Once the beetle has hatched, it remains in the old larval skin for two to three months if the external conditions are unfavorable. Only in spring do they break free and swarm to daylight to find food. Such carpet beetles have a life expectancy of a few days. If the insects only stay in the last larval skin for three weeks, their lifespan can be extended to a month. This also depends on the food supply and water availability, so slight fluctuations are possible.
Why are carpet beetle larvae useful?
They decompose remains that are no longer eaten by other living beings. Carpet beetle larvae can digest dry remains of dead animals such as cartilage, hair, feathers or claws. Therefore, carpet beetles prefer to lay their eggs in bird nests with feathers or dead baby birds.






