- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-24 06:09.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced hobby gardener: When setting up a vegetable garden, there are many things you need to consider so that you can enjoy a bountiful harvest as soon as possible. The following article provides instructions as well as many tips and tricks from large self-sufficient to small potted gardens.

How do I create a vegetable garden correctly?
To successfully create a vegetable garden, choose a sunny or partially shaded location, plan the size and design of the beds, pay attention to the soil condition and create a planting plan that takes mixed culture and crop rotation into account.
Creating a vegetable garden for beginners
Unfortunately, it is not enough to simply dig up a piece of garden and plant vegetables on it; No matter whether you just want to create a vegetable patch or a large kitchen garden. In order for zucchini, tomatoes, etc. to grow well and produce lots of delicious fruit, they need the right conditions for their growth. You can create this by carefully planning your future vegetable garden and selecting the optimal location. The following chapters will show you how this works and what you need to pay attention to.
The following short video also provides great tips for easily creating and planting vegetable beds:

Location
You don’t need an ominous “green thumb” to garden successfully. Enthusiasm, affection and attention are completely enough.
By the term “location”, the gardener primarily means what lighting conditions prevail in the area intended for the vegetable patch. A rough distinction is made between:
- Full sunny: every day the sun shines unhindered on the bed for at least six hours
- Sunny: Sunshine duration at least four hours a day
- Off sunny: bright, but not exactly sunny
- Partly shaded: Sunshine lasts up to four hours a day, especially in the morning or evening
- Light shady: Bed is temporarily shaded
- Full shade: Bed is permanently in the shade
Locations that are partially shaded to sunny are ideal for a kitchen garden. Full sun beds are only suitable for vegetables that require a lot of heat, such as tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, etc., and also pose the risk that the plants in them will dry out quickly, especially on hot days.

Vegetables need a lot of sun to grow well
Sunny to partially shaded locations, on the other hand, offer the best conditions for most vegetables and herbs, especially if the beds are shaded during the hot midday period. Lightly shaded beds, on the other hand, are only suitable for a few crops, as the light intensity necessary for fruit development and ripening is often not achieved. For this reason, you should never plant vegetable beds under trees or similar places.
Which plants for which location?
The table below provides you with a practical overview of the optimal location for some of the most popular vegetable plants.
| Sunny | Partial shade to light shade |
|---|---|
| Aubergines | Asian salads (Pak Choi, Mizuna) |
| Beans | Leaf lettuces, pick and cut lettuces, cauliflower, broccoli |
| Chili | Lamb lettuce |
| Cucumbers | Garden cress, kale |
| Potatoes | Garlic, kohlrabi, leek |
| melons, carrots | Swiss chard and other leafy vegetables (e.g. turnips), parsnips |
| Peppers | Sorrel, spinach |
| Radish | Radish, rhubarb, beetroot, Brussels sprouts, rocket |
| Tomatoes | White cabbage and other types of cabbage |
| Zucchini, sugar peas | Onions |
Size and time required
This point is particularly important and worth considering for those new to gardening, because the daily workload of a large kitchen garden is often greatly underestimated. Remember that a garden like this requires a lot of planning, care and physical effort - and you must therefore have both the necessary fitness and the time for it. Digging up vegetable beds is tiring, but planting and weeding can quickly make your back hurt.
Thus, consider
- What you want to do with your vegetable garden: Are you planning a self-sufficient garden because you no longer want to buy vegetables in the supermarket or do you just want to grow a few special types? Or even start your own cultivation of old vegetables?
- How much time you can spare: For every ten square meters of garden you should spend approx.plan half an hour of work. For a kitchen garden of around 400 square meters, this results in a total effort of around 20 hours - which also extends to almost every day of the week, including the weekend.
- What your physical fitness is like: A vegetable garden not only takes time, but also physical effort. If you have problems with your back and/or knees, raised beds are recommended instead of the classic garden beds.
Excursus
How big does a self-sufficient garden have to be?
If you want to provide your family with fresh vegetables from your own garden, plan on at least 20 square meters for each person eating. For a family of four, such a kitchen garden should be 80 square meters in size, although the area for fruit trees is not included here. If you also want to harvest apples and berries, an additional 20 square meters of space is required.
Soil texture

Most plants prefer loose, nutrient-rich soil
Most crops have a medium to high nutrient requirement and therefore prefer a humus-rich, nutrient-rich soil. This should also be loose and deep so that roots and vegetables growing underground have enough space to grow. Solid, clayey soils, on the other hand, tend to become waterlogged and are therefore less suitable. However, just like poor soil, they can be improved with appropriate measures. This includes, for example, creating drainage and adding compost or good topsoil.
Create a vegetable garden in the new development area
Such soil improvement is particularly important in new development areas, as the soil here is heavily compacted due to the use of heavy machinery and needs to be loosened. It may also sometimes be necessary to remove the upper layers of earth and refill them with fresh topsoil - the remains of various building materials, especially those containing lime, quickly become embedded in the soil and upset the acid-base balance. Basically, the soil in a vegetable garden should have a pH value that is as neutral to slightly alkaline as possible so that the plants can optimally absorb nutrients and moisture. Please also note that some plants cannot tolerate lime and only a few species thrive in acidic soil.
Create beds and paths
Vegetable plants grow in specially designed beds that are usually rectangular. Narrow paths run between the beds to ensure access to the overgrown areas - after all, the plants need to be looked after and nurtured so that you can look forward to a bountiful harvest later. Regarding the size and length of the beds, there are certain guidelines that should make it easier for you to work on the areas:
- Vegetable beds should not be wider than 120 centimeters
- this makes it easier to maintain and harvest the areas, as you can easily reach anywhere
- small people should reduce the bed width again
- The length of the beds, however, is entirely up to your own wishes and the available space
- However, it makes sense for all vegetable beds to be of the same size
- this makes planting planning easier even in later years
- a good bed size is six square meters (1.20 meters wide x 5 meters long)
- 25 such beds plus paths fit into a 150 square meter vegetable garden
The paths divide the bed areas evenly into segments, although the side paths remain quite narrow at around 60 centimeters wide. The main paths should be planned and paved a little wider at around one meter so that you can walk along them comfortably with a wheelbarrow.
Tip
Never plant the vegetables directly on a hedge, because they will not grow well here anyway due to the shadows and the competition for water and nutrients. Instead, create a path between the bed and the hedge, also because you have to be able to reach the hedge easily for trimming anyway.
Create a compost site
Compost is essential for every vegetable garden, after all, the plants need a lot of nutrients for their growth and the development of their fruits. With your own compost heap, you provide valuable, biological fertilizer and at the same time return organic waste to the natural cycle. A win-win situation for both you and nature. When planning the compost site, the following tips are useful:
- not too small: Space for at least three sufficiently large compost containers is necessary
- easily accessible: Compost site should be easily accessible from the main path
- shady location: the compost site is best located in the shade of a large tree so that it does not dry out too quickly during the hot summer months
- slightly away from the vegetable beds: place the compost on the north side of the kitchen garden so that the containers do not cast shadows on the beds
Do not seal the substrate of the compost site, as earthworms and other soil creatures are essential for decomposing the material and converting it into humus. These penetrate the compost through the soil.
Irrigation

Drip irrigation saves work and water
Irrigation is essential for the vegetable garden because without an adequate supply of water, all plants will die. Insufficient irrigation also ensures that the fruits remain small and the harvest is correspondingly poor. If you don't want to constantly lug around heavy watering cans, you can install special irrigation systems in the garden. These are usually connected to the main water pipe (if one exists) and run underground next to the main paths. It is best to create the selected system at the same time as the beds and paths in order to save yourself multiple work.
Create planting plan
So that you can make optimal use of the available bed space throughout the entire season, you should draw all the beds and paths on a plan and determine when and where which vegetables should be planted or sown. The following tips will help you:
- Mixed culture: Do not plant monocultures in the garden, but combine different vegetable plants in one bed. This serves plant he alth because pests and pathogens have little chance of spreading. However, keep in mind that not all plant species get along. Mixed culture tables give you a good overview of who goes together and who doesn't.
- Follow-up culture: The different types of vegetables sometimes grow at very different times. While some ripen at the beginning of the year, others can only be planted in the bed in the summer. With a so-called follow-on crop, you can use the vegetable patch all year round, for example by planting spinach and radishes in spring and then zucchini in summer. But the same applies here: Some plant species do not get along, which is why vegetables from the same plant family are not allowed to follow each other.
- Nutrient requirements: Divide your beds into three sections, in which you cultivate heavy feeders, medium feeders and weak feeders separately and change the beds every growing season. This means the soil doesn't leach out excessively, but can instead recover from time to time.
You can find a practical example of a successful mixed and subsequent culture with Phacelia as green manure in this illustration:
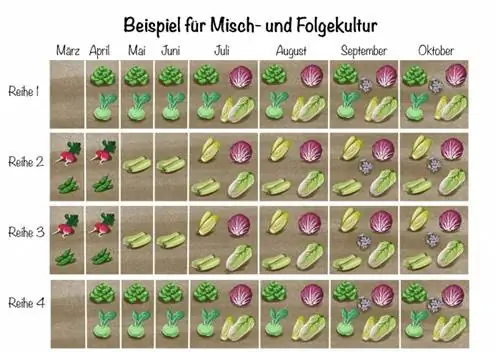
Creating a vegetable garden - examples and ideas
No question: simple, rectangular vegetable beds with side paths and a well-paved main path are easy to plant and maintain. This traditional shape has long since proven itself and is still popular today - it becomes particularly pretty when the individual beds are surrounded by low box hedges, as has always been done in classic cottage gardens. But herbs and low perennials (e.g. lavender, marigolds, marigolds, etc.) are also very suitable for fencing.
If that's too boring for you, you can also create the vegetable beds round, oval, triangular or in other shapes or use systems such as hill beds, straw beds or layered beds. Modern raised beds or lower box beds, for example, are good and practical, especially for small gardens. Vegetable beds can also be placed in tractor tires and other more unusual enclosures.
Cuttable garden or mixed beds?
Nasturtiums, marigolds, marigolds, lavender and other flowers not only look pretty, but also provide valuable support for the vegetable plants in the kitchen garden: lavender, for example, reliably keeps aphids away, and nasturtiums also drive away various common garden pests - and are also valuable Snail attractant plant. The voracious reptiles love to feast on the bushy nasturtiums and leave your vegetable plants alone. Tagetes - the marigold flower - is also an effective distraction food and at the same time keeps flies and even voles away. Therefore, plant not only useful plants in your vegetable garden, but also various (supposedly) ornamental plants.
Frequently asked questions
When is it time to plant vegetables?

If you want to harvest early, you should prefer cold-sensitive plants in warm conditions
When different vegetables are planted or sown depends on various factors. One of the most important is the plants' natural resistance to cold: some plants thrive in early spring or even late autumn, while others are only allowed into the bed after the last late frosts. The information on the seed bags or on the labels for purchased young plants provides reliable clues for the best planting time.
Which vegetables and herbs can be cultivated on the balcony?
If you only own a small garden or even just a balcony or terrace, you still don't have to do without your own garden. Almost all vegetables and herbs can be grown in buckets, pots, boxes and other containers, but they require a lot of attention. Regular watering and fertilizing is extremely important because the plants cannot take care of themselves. The cultivation of irrigation-intensive and very large vegetable plants such as zucchini can therefore be difficult - but not impossible.
Which vegetables are suitable for children?
All fast-growing snack vegetables such as radishes, carrots, sugar peas etc. are very suitable for children, as the little ones have quick success with them and can eat the harvested vegetables straight away.
Which plants keep pests away?
Not only do some flowers such as marigolds, nasturtiums and the like keep pests away from the vegetable patch, allium plants such as onions, garlic and leeks also have a deterrent effect on uninvited visitors and many pathogens. Please note, however, that onions and garlic do not harmonize with some other vegetables and should therefore not be planted together.
Tip
From the beginning, write down which vegetables you planted in which bed and when. This way you can keep a better overview and plan crop rotation more easily in the coming years.






