- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:19.
Biological pest control in the house and garden makes sense because you avoid using poison and therefore do something good for yourself and the environment. The parasitic parasitic wasps are extremely helpful against all kinds of pests.

- Parasitic wasps are parasitic beneficial insects that lay their eggs in the larvae of harmful insects.
- There are numerous different species, often specializing in certain host species.
- That's why only certain parasitic wasps can be used against moths, aphids, whiteflies, scale insects and other pests.
- The application should be carried out over a period of several weeks, with the cards containing parasitic wasp eggs from specialist retailers being laid out several times.
What are parasitic wasps?
When the name “parasitic wasps” comes to mind, many people first think of real wasps, which are particularly annoying in late summer and can be quite persistent in their search for sweets. However, the useful parasitic wasps have nothing in common with the Vespinae species apart from their name (and sometimes also their external appearance - the males of some species engage in mimicry). Instead, like bees and bumblebees, they also belong to the hymenoptera family (lat. Hymenoptera).
There are around 40,000 different species of parasitic wasps that live in a wide variety of habitats and can look quite different. The smallest varieties reach a body length of less than a millimeter and are practically invisible to the naked eye. Other species can be between one and five centimeters long.
What all parasitic wasps have in common is their parasitic lifestyle, as the females generally lay their eggs in the eggs of other insect species. The larvae that hatch from this in turn feed on the host larvae and destroy them. Since most species of parasitic wasps specialize in pests in the home and garden, the animals are extremely useful for biological pest control. The adults, in turn, feed mainly on pollen, nectar and honeydew.
Appearance
The parasitic wasps probably owe their name to the fact that the male specimens of some species can actually be confused with true wasps. However, this is just a tactic known as mimicry, which is intended to protect against predators. In general, you can recognize parasitic wasps by these characteristics:
- mostly dark brown to black basic color
- often colored (red) or white spots or stripes
- dark, translucent wings
- movable, long wings
- typical “wasp waist”
- long ovipositor spine, which can be as long as the actual body
- This only occurs in females and is used to lay eggs
- depending on the species, body length between 0.2 and 50 millimeters
Lifestyle
“The behavior of parasitic wasps may seem brutal, but it is very helpful for humans.”
Parasitic wasps are among the so-called egg parasites. The female animals have a keen sense of smell, which they use to track down and target the larvae of their host animals - for example moths, butterflies, wasps, beetles, aphids, flies or even spiders. They then parasitize their host animals, which proceeds as follows:
| Development phase | This happens: |
|---|---|
| before laying eggs | Injecting a toxin into the host larva to paralyze it |
| during egg laying | Injection of the egg into the host body using the ovipositor stinger |
| after laying eggs | Hatching inside the host body and pupation; Host bodies are often bloated and dark brown to black in color |
| Nutrition of the larvae | Host body is eaten from the inside |
| after pupation | The adult parasitic wasps drill a hole through the host's body and from there slip out into the open |
Biological pest control in the home and garden

Parasitic wasps eat their prey out of the egg
The parasitic lifestyle of parasitic wasps as well as their specialization in specific pests in the house and garden make the animals ideal helpers. The beneficial insects not only combat food and clothes moths effectively and without poison, but also aphids and scale insects, whiteflies or butterflies such as the codling moth, leaf miners or the oak processionary moth. In agriculture, the beneficial insects are often used on a large scale to prevent crop failures caused by pests.
Tip
If you use parasitic wasps in the garden or greenhouse, be sure to leave the parasitized larvae in place. A new generation of parasitic wasps is growing here, which will keep you away from another pest invasion.
Overview: You can use parasitic wasps to combat these pests
Given the large number of different species of parasitic wasps and the fact that they often specialize in certain pests, you cannot use just any variety. Depending on which pest you want to combat, these types of parasitic wasps come into question:
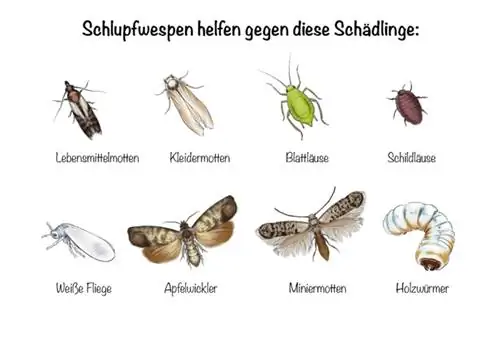
| Type of pest to be controlled | Suitable parasitic wasp species |
|---|---|
| Food Moths | Trichogramma evanescens |
| clothes moths | Trichogramma evanescens |
| Aphids | Aphelinus abdominalis, Aphdius colemani, Aphidus ervi, Aphidus matricariae |
| Scale insects | Metaphycus flavus, Microterys flavus, Coccophagus lycimnia |
| Whitefly | Encarsia formosa |
| codling moth | Trichogramma cacoeciae |
| Leaf miners | Encarsia formosa |
| Woodworms | Spathius exarator |
The tiny Trichogramma species are mostly used in agriculture and commercial fruit growing. But be careful when using parasitic wasps outdoors: the animals can in turn become infected with parasites or pathogens, or fall victim to toxins or predators (e.g. birds). Then their effect is only limited.
Parasitic wasps against bacon beetles?
Occasionally, the use of parasitic wasps is also recommended against various types of so-called bacon beetles, although experiences here vary greatly. Instead, it is better to use camp chalcid wasps (lat. Lariophagus distinguendus) or bacon beetle wasps (lat. Laelius pedatus). These two species of beneficial insects are also egg parasites that do not build their own nest.
Excursus
Are parasitic wasps dangerous?
Parasitic wasps are in no way dangerous to people or pets and can therefore be used safely in the home as well as in the greenhouse or in the garden. The useful animals only stay where they can find food and reproductive opportunities in the form of insect eggs.
Advantages and disadvantages of parasitic wasps

Treatment with parasitic wasps has both advantages and disadvantages
Like so many things, the use of parasitic wasps against pests also has advantages and disadvantages. How you weight these is entirely up to you. In principle, however, biological control measures such as the release of beneficial insects make sense because they save a lot of poison - and this in turn has positive effects on people and the environment. Don't forget that insecticides always have harmful effects on yourself and other living beings!
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| non-toxic, without chemicals | relatively long treatment time |
| Rooms can continue to be used during treatment | must be reapplied regularly due to their short lifespan |
| Parasitic wasps can be easily lured into the garden and settled there | strong specialization of individual species on certain pests |
| Use against many different pests possible | Parasitized pest larvae should not be collected or removed |
| also preventive use (e.g. in orchards, in storage rooms) | |
| uncomplicated application |
Where can you buy parasitic wasps?
You do not buy parasitic wasps in the form of live animals, but rather as eggs applied to special cards. When used, the finished beneficial insects finally hatch from these and in turn lay their eggs in the larvae of the pests to be combated. The parasitic wasps come from laboratories in which the animals are constantly bred under ideal conditions.
You can order the egg cards in specialized shops on the Internet as well as from larger shipping portals such as Amazon and eBay, but you can often also purchase them in garden shops, nurseries, hardware stores, natural stores or drugstores such as DM. Parasitic wasps of the genus Trichogramma are mostly available, but for more specific species you often have to search a little more intensively.
The advantage of online retailers who specialize in beneficial insects is that they send you new egg cards at regular intervals (usually three weeks) and you don't have to constantly try to buy a new one yourself. Since it is not possible to keep stocks and the cards have to be reissued over a longer period of time, this service makes sense.
How much do parasitic wasps cost?
When it comes to costs, the different providers vary, but on average you should expect to pay around 30 EUR for three deliveries of four cards each. When purchasing, make sure that the cards contain more than just 300 to 400 parasitic wasp eggs: This number is usually not enough for the successful fight against clothes and food moths.
Insert and use parasitic wasps
This clear video explains very well how the use of parasitic wasps works:

Using the parasitic wasp cards is very easy: just lay them out or hang them up and wait. Everything else happens by itself! However, make sure that you do not use intense scents (such as the essential oils recommended against moths), harsh cleaning products, etc. during this time, as these also have negative effects on the parasitic wasps and therefore influence the success of the treatment. Also make sure that the room temperature and humidity do not fluctuate too much, as the parasitic wasps react quite sensitively to this.
Tip
You should never leave parasitic wasp cards with eggs of the Trichogramma species hanging freely anywhere: these little animals can only crawl, but cannot fly and therefore need a firm hold.
Against food moths
Food moths are a problem in many households and are rarely due to poor hygiene. Most of the time you simply drag the animals home with your shopping, where they happily multiply. The infestation is not only unsavory, but also a he alth risk. Although food moths and their larvae are not poisonous themselves, they can cause allergic symptoms. They also contaminate food with their excrement. There are different species - such as the flour moth (Ephestia kuehniella), the corn moth (Nemapogon granella), the dried fruit moth (Plodia interpunctella) or the rice moth (Corcyra cephalonica) - which can all be controlled very well with parasitic wasps.
And this is how it works:
- Buy parasitic wasp cards for food moths.
- These should contain about 3000 to 4000 eggs.
- Do not store the cards, but attach them immediately after receiving them.
- Place the cards in the immediate vicinity of the identified infestation.
- You should plan one card per shelf compartment or drawer.
- Repeat the application three times at intervals of three weeks.
Also remove food contaminated with moths and moth eggs to prevent the plague from spreading further.
Excursus
You can still do this against moths

Lavender bags are good protection against parasitic wasp infestation
An infestation with food or clothes moths can usually hardly be avoided, as the animals are often brought in when shopping - a bag of flour contaminated with moth eggs is enough! Clothes moths, on the other hand, usually enter the house through a window that is open for ventilation. However, you can take a few precautions to ensure that the animals don't stand a chance: For food, easily sealable containers made of glass or metal, for example, help to keep the pests away. Plastic or paper packaging, on the other hand, is unsuitable because the larvae can bore through them. In the wardrobe, scents such as lavender, lemon oil, cedar wood and other intense smells drive away the pests.
Against clothes moths
The clothes moth (lat. Tineola bisselliella) is a moth that is widespread all over the world. The pest is very small, only measuring between six and nine millimeters. Since the larvae feed on keratin, proteins found in animal hair fibers, clothing made from natural fibers such as wool is particularly at risk. The moth lays its eggs directly on clothing and the larvae that hatch from them leave unsightly feeding holes. An infestation can often be recognized by the typical musty smell.
To successfully combat clothes moths with parasitic wasps, it is best to proceed as follows:
- First remove all clothing that is visibly infested with moths.
- Reduce moth infestation in this way.
- Wash the textiles at least 60 °C or freeze them for 24 hours.
- This also kills the moths and their eggs.
- Place the parasitic wasp cards between the items of clothing or attach them to them.
- The cards are not allowed to hang freely!
- Use one card with at least 3000 parasitic wasp eggs per shelf compartment.
Since clothes moths are very stubborn, you should carry out the treatment over a period of 15 weeks and reapply fresh cards a total of six times, every three weeks apart.
Parasitic wasps against pests in the garden and greenhouse
Parasitic wasps can not only be used in the apartment or house, but also provide useful services in the garden and greenhouse. Here you can use the animals in combination with other beneficial insects - such as ladybirds and lacewings. However, this only works if you avoid using chemicals in the form of pesticides, insecticides, etc. outside. These not only kill the pests, but also the desired beneficial organisms and thus disrupt the biological balance. The animals are also suitable for preventing pest infestation on endangered plants such as tomatoes or cucumbers.
And this is how it works:
- Put out the cards with the parasitic wasp eggs as early as April if possible.
- Place them directly on the affected or endangered plants.
- For prevention, cards with around ten to 15 eggs per square meter are sufficient.
- Of course, to combat a current plague you have to use significantly more animals.
- Here the guideline value is approx. 3000 eggs per card placed.
Fighting with parasitic wasps works best in summer, when temperatures are constantly at 20 to 27 °C and humidity is around 60 percent. Under these conditions the parasitic wasps reproduce very quickly. However, if it is too cold, the treatment often has little or no success - the more robust pests then multiply faster than the parasitic wasps. Therefore, when temperatures are cooler, you also use other beneficial insects or limit the use of parasitic wasps to indoor areas or the greenhouse.
How to attract parasitic wasps to the garden

Adult parasitic wasps feed primarily on flower nectar and pollen
Some species of parasitic wasps are native to this country and - provided the living environment is right - can be lured into the garden and settled there with a few tricks. These species are particularly valuable for the natural control of common garden pests such as aphids and scale insects. Read this section about what these parasitic wasps need to feel comfortable in your garden.
- Food sources: Although parasitic wasp larvae are parasitic and therefore dependent on host animals, adult animals feed primarily on the pollen and nectar of umbelliferous plants. Therefore, you should preferably cultivate appropriate plants in your garden to attract the animals.
- Suitable umbelliferous plants: Many herbs and useful plants such as fennel, anise, lovage, dill, chervil, carrots and parsnips belong to this group, but also pretty ornamental plants such as the shade-tolerant sweet umbel (Myrrhis odorata), the sun-hungry cow parsley (Anthriscus sylvestris) as well as extremely popular flowering plants such as ivory man litter (Eryngium giganteum), ornamental onions and peonies. Hardly any other plant genus attracts more beneficial insects than these!
- Insect Hotel: Of course, suitable accommodation should not be missing, even if the animals do not build nests due to their lifestyle. An insect hotel near flowering umbelliferous plants, in a sheltered and warm place, attracts numerous other insects. Parasitic wasps prefer small pieces of wood with tiny drill holes (diameter between two and eight millimeters), which you lay out or hang in the trees as early as possible in the year. These woods are also often used for overwintering.
Can I breed parasitic wasps myself?
Typical parasitic wasps found in the garden can be attracted by creating a suitable habitat. Others, such as the Trichogramma species, must be bred in the laboratory under suitable conditions. If you want to save money, you can of course try this yourself - but the chances of success are not particularly high. Pay attention to these conditions:
- constant temperatures between 18 and 20 °C
- Humidity of around 60 percent
- sufficient moth eggs as food
- Put moth eggs and parasitic wasps together in a jar
- Cover glass with linen cloth
- Incubator is ideal for breeding
- Start temperature 25 °C
- slow drop to 18 °C
- permanently add new food (moth eggs)
- Parasitic wasps immediately start looking for new eggs after they hatch
The animals can be produced much more cost-effectively in industrial laboratories. For a private consumer, breeding parasitic wasps involves a lot of effort, which is not always successful - the beneficial insects are too sensitive for that.
Excursus
Can I use parasitic wasps and insecticides at the same time?
No question, the temptation is great when there is a massive moth infestation. But under no circumstances should you fight a pest invasion with parasitic wasps and insecticides at the same time! In this case, you would not only kill the pests, but also the beneficial insects you used. These in turn would not be able to fulfill their task at all.
Instead, stick to the manufacturer's recommendation regarding the amount of parasitic wasp tablets used and the recommended duration of treatment, then you will quickly get rid of your pests.
Frequently asked questions
Do parasitic wasps survive in extreme heat or cold? How do I know if they will survive shipping?
You can order parasitic wasps without hesitation even in winter or during the hottest summer heat. The manufacturer or retailer will adjust the packaging accordingly or send you the desired shipment at a more convenient time. But no matter what weather conditions are currently prevailing: Do not leave the parasitic wasps lying around for days (especially not in an outdoor mailbox!), but distribute them as soon as you receive them. Buying in advance is therefore not possible and does not make sense. You should only buy the animals if you want to use them directly.
What happens to the parasitic wasps when the pest infestation is eliminated?
You don't need to worry that parasitic wasps will bring a new insect plague into your house orbring into the garden. The useful animals only survive as long as they have enough food and reproductive opportunities in the form of their favorite insect eggs. Since most species are specialized on certain pests, they die due to the lack of food (i.e. when there are no more pest eggs left) or migrate to more profitable areas, for example through an open window.
How long do parasitic wasps survive?
Parasitic wasps only have a very short lifespan: depending on the species, the adults reach an age of between a few days or weeks. In the case of the Trichogramma parasitic wasps used on food and clothes moths, it is actually the case that they live significantly shorter than the moths themselves. For this reason, you must plan the application so that you can use it over a total period of nine or 15 weeks Lay out new cards every three weeks.
Can parasitic wasps sting?
In contrast to real wasps, which can spoil your outdoor coffee table in late summer and can even sting if threatened, parasitic wasps are not interested in cakes, people or pets. With their extremely fine sense of smell, the animals detect the eggs of their preferred host animals and go to them immediately. However, parasitic wasps do not sting or bite, so there is no danger to humans or animals (at least not if it is not an insect favored by parasitic wasps).
Tip
The parasitic wasp species Lysiphlebus testaceipes is particularly suitable for combating aphids, as the animals emit a scent very similar to aphids and are therefore not recognized and attacked by ants - who like to keep aphids as "pets".






