- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
Behind organic fertilizer there is a complex product that activates various soil processes. Although remedies are available commercially, everyone should think about making their own. This is neither heavy nor expensive, because plants form the basis of a good fertilizer.

What is organic fertilizer and how is it made?
Organic fertilizer consists of animal or plant residues and provides nutrients for plant growth. Compared to mineral fertilizers, they work more slowly and improve the soil structure. Organic fertilizers can be made yourself, for example from compost, plant manure or green manure.
What is organic fertilizer?
If a fertilizer is of organic origin, then dead organisms and their excretions provide the fertilizing components. They are made from waste materials from agriculture or private gardening. The nutrients are not present in pure form, but are mostly bound to carbon-containing compounds.
These are organic fertilizers:
- Manure, manure or manure
- Sewage sludge
- Green manure
- Compost and straw
Nutrient content of organic fertilizer

Organic fertilizers are rich in important nutrients and life
Organic fertilizers contain the main nutrients nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (NPK for short) and a number of other trace elements, proteins and vitamins. Nitrogen is contained in various forms. The total nitrogen content includes organically bound nitrogen, which has to be decomposed by soil organisms, as well as immediately available nitrogen compounds such as ammonium nitrogen. These compounds are available to plants in the first year. The nutrient contents vary depending on the substrate.
| Nitrogen content | effective nitrogen content in the first year | Phosphorus content | Potassium content | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compost from leaves and green waste | 6 kg/t | less than 1 kg/t | 2 kg/t | 4 kg/t |
| Horse manure | 4 kg/t | 2 kg/t | 3 kg/t | 11 kg/t |
| Horn shavings | 140 kg/t | 1 kg/t | 8 kg/t | 1 kg/t |
| Organic waste | 9 kg/t | less than 1 kg/t | 5 kg/t | 8 kg/t |
| Bark mulch | 3 kg/t | insignificant | less than 1 kg/t | 1 kg /t |
How does organic fertilizer work?
The composition of the material determines how quickly the organic fertilizer works. The C/N ratio is the ratio between carbon and nitrogen and provides an orientation for the rate of action. The more organically bound nitrogen there is, the slower the fertilizer works. This must be mineralized in the soil, which first releases ammonium compounds and finally nitrate.
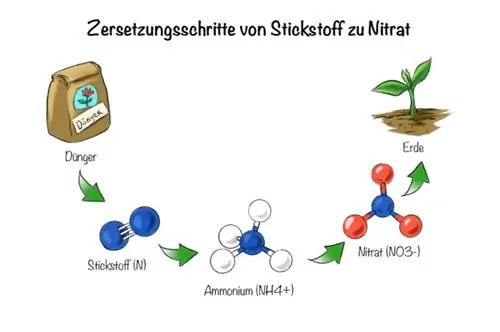
Nitrate can be absorbed by plants. Conversely, this means that the more nitrate and ammonium nitrogen it contains, the faster the fertilizer works. Manure is an example of a particularly fast-acting organic fertilizer. It is similar to a dissolved mineral fertilizer.
Ammonium nitrogen content in:
- Manure: about 50 percent
- Stable manure: ten to 20 percent
- Compost: around five percent
Background
Mineralization and humification
When microorganisms utilize organic material, various processes take place. The decomposition of organic material in soil is called humification. The plant and animal remains are not broken down, but are broken down and converted by soil organisms. This creates humic substances, which form the basis of humus. These organic fragments are broken down and finally broken down by enzymes from various microorganisms. This creates mineral end products that can be used by the plants. This process is called mineralization.
Influencing factors
The implementation of organic fertilizer depends on the weather, because the active soil organisms are strongly influenced by their environment. A moist environment with warm temperatures and good oxygen supply promotes the conversion of the material. Cold, wet conditions and a lack of oxygen inhibit the activity of soil fauna.
Organic NPK fertilizer
Organic fertilizers can also be processed industrially so that they contain natural substances and synthetic nutrients. They are less concentrated than mineral NPK fertilizers and can be applied in liquid form or as granules. When used regularly, the soil is improved because organic commercial fertilizers build up the humus layer. On the one hand, they contain immediately effective nutrient s alts as well as components that release nutrients over a longer period of time.
This is what organic commercial fertilizers contain:
- animal origin: Flours made from animal skeletal parts such as meat bones and horn; Hair meal pellets, feather meal
- vegetable origin: water and concentrates from potato plants, remains of corn processing, vinasse, m alt germ
- other organic NPK fertilizers: Biosol, legume fertilizer, hydrolysates
Application
Organic fertilizers must be lightly incorporated into the top layer of soil so that they can develop their full effect. Microorganisms attack the components from all sides and decompose them so that the nutrients are made available to plants. When distributed superficially, the nitrogen content is predominantly broken down. The material should also not be worked in too deeply, as rotting processes occur in the absence of air.
Organic fertilizer for lawn

Organic fertilizer is also a good choice for the lawn
The nutrient supply via organic fertilizers can not only be used for herbs in the bed. They also provide the lawn with vital substances so that it thrives. However, solid substrate is not suitable for fertilizing an existing lawn. In this case, liquid alternatives are necessary because compost can no longer be incorporated into the soil. Organic commercial fertilizers in liquid form are still better than mineral fertilizers.
| organic lawn fertilizers | mineral lawn fertilizers | |
|---|---|---|
| Humus layer | promote the formation of humus | Decomposition of humus when used excessively |
| Ground activity | Soil organisms are encouraged | reduce the diversity of soil fauna |
| Effect time | Long-term effects | quick and direct effect |
| Application | Compost only in front of the lawn; organic liquid fertilizer on vegetated areas | three times a year on overgrown areas |
| other | often contaminated by heavy metals or pesticide residues | enriched with weed-inhibiting additives |
Buying organic fertilizer - what to look out for?
Laboratory tests have found heavy metals, pollutants and pesticides in organic fertilizers from various price ranges. A sample from the magazine “Öko-Test” (can be read in the July 2017 issue) states that even most organic products are not perfect. If you want to buy organic fertilizer, you should know exactly where it comes from.
Even organic fertilizers are not perfect. They may contain pollutants and heavy metals.
Soil fertilizer or plant fertilizer?
Fertilizers suitable for soils predominantly contain stable carbon compounds that are broken down over a longer period of time. They increase soil fertility slowly and sustainably because they act as long-term fertilizers. Mineral fertilizers are completely out of the question as soil fertilizers because they have a short-term effect and the nutrients are washed out. The situation is different in the group of plant fertilizers. Organic NPK fertilizers provide directly available nutrients and offer long-term effective substances. In contrast to mineral products, they increase the crumb structure.
Tips for decision-making:
- Granules and pellets are easier to distribute and do not form dust
- Substrates from composting plants are inexpensive and have an optimal nutrient composition
- Group plants with similar needs and choose a suitable fertilizer accordingly
Plant or animal?

Manure usually smells very strong
Organic fertilizers are waste products and are therefore the optimal choice in terms of sustainability. If the degradable residues come from plant raw materials, they often provide better nutrient mixtures than animal products. The production of plant-based raw materials requires little space and requires less water. When it comes to fertilizers made from animal residues, it is often not clear whether the raw materials come from organic or conventional animal husbandry. The odor nuisance is greater with ground animal residues than with purely plant-based products.
Tip
Coffee grounds are a real source of nitrogen and are also free from animal products.
Organic fertilizer - advantages and disadvantages
Natural fertilizers based on plant or animal residues improve the structure of the soil and promote humus formation. Due to their slower action time, the nutrients from organic fertilizers are washed out less quickly than mineral alternatives. They provide the plants with nutrients over a long period of time without over-fertilizing the soil. Plants receive sufficient nutrients during their main growth phase, because during this time the soil organisms are more active than in cold months.

Disadvantages:
- Fertilizer requirements are difficult to calculate in advance
- not suitable for correcting an acute nutrient deficiency
- animal products often only contain one or two main nutrients
From an ecological perspective
Many soils already have an excess of nitrogen, which places a heavy burden on sensitive habitats. This imbalance means that certain plant species are pushed back and only those that predominantly need nitrogen to grow dominate. Fertilizing with organic substances from your own garden does not introduce any new nitrogen into the ecosystem. A balanced cycle is created in which nutrients are recycled.
Make your own organic fertilizer

Plant manure is a great fertilizer
Compost is considered an all-rounder among natural fertilizers. The substrate provides the plants with calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and potassium. Weak-wasting plants thrive if they are occasionally given a little compost. But even heavy feeders grow better with regular compost additions.
Tip
Herbs with large and soft leaves enjoy a slow-release fertilizer. Pellets made from sheep's wool are ideal for potted plants.
Plant manure
Collect wild herbs such as nettles, tomatoes, yarrow and comfrey and roughly chop the plant parts. Place the material in a bucket and fill it with water until all parts of the plant are covered. Cover the container with a cloth and stir the mixture every two to three days.
The manure is ready after about two weeks. No more bubbles should appear when stirring, as gas bubbles indicate ongoing activity by microorganisms. During the fermentation process, various nutrients are released from the plant parts. Plant manure is rich in silica and trace elements.
- Rock dust or algae lime suppress unpleasant odors
- Plant manure is suitable for heavy feeders such as tomatoes and potatoes
- Application diluted five to ten times with rainwater
Green manure
If beds lie fallow and will not be used again until the coming season, you can use them for a fertility-promoting cover crop. Pay attention to relationships, because species from the same families should not grow one behind the other on the same bed. Shortly before seeds form, the beds are mowed, leaving the plant material on the surface. Green manure loosens the soil. At the same time, weeds are suppressed and the soil is protected from erosion and leaching.
Suitable seeds

Mustard is ideal for green manure
Sow yellow mustard in areas that will not subsequently be planted with cabbage or cruciferous vegetables. The fast-growing yellow mustard is ideal as a precursor to potatoes. The blue-flowering Phacelia is not closely related to any type of vegetable and can therefore be sown universally. Legumes such as clover, lupine, vetch or winter peas are ideal sources of nitrogen.
Frequently asked questions
Which fertilizer is suitable for which plant?
A nitrogen-based fertilizer is the typical green manure. It is suitable for all plants that need to develop he althy foliage. Horn shavings and coffee grounds are ideal nitrogen suppliers for lawns, cabbage and lettuce or houseplants. On the other hand, a phosphorus-based fertilizer is ideal for flowering plants because this nutrient promotes flower and fruit development. Provide flower bulbs, violets and fruit trees with manure from chickens and poultry.
Why are organic fertilizers better for crops?
Potato, zucchini and cabbage are among the heavy eaters that require a lot of nutrients throughout the entire growth phase. Chemical products work immediately, so plants are often over-fertilized. The excess nutrients are quickly washed away by rain, creating a nutrient deficiency. Organic fertilizers feed the plants evenly over a long period of time.
What are the signs of incorrect application of mineral fertilizers?
When using mineral fertilizers, you can often observe the effects of incorrect use. The nutrients are in the form of water-soluble s alts. The s alt removes water from the plant cells, which is why the plants often leave their leaves hanging after fertilization. In order to reduce the s alt content in the substrate, extensive watering is necessary.
Can organic fertilizers be used incorrectly?
Natural fertilizers should also be applied with caution, as incorrect nutrient additions quickly lead to deficiency symptoms or unbalanced plant growth. If the phosphate content is too high, other nutrients can no longer be absorbed. An oversupply of nitrogen causes strong leaf development, which stagnates flower formation.
Is the pH value in the soil important for organic fertilizers?
Low-nutrient sandy soils require more nutrients than subsoils rich in humus. But even after increased fertilizer application, plant growth can stagnate. If this is the case, you should check the soil pH. Many nutrients can no longer be absorbed by plants if the pH is too high. In this case, the soils should be treated with acidic substrates before fertilizing. If the pH value is acidic, the plants can hardly absorb nitrogen. Adding lime improves the soil.






