- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2024-01-07 16:36.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:19.
Cellar rattles are disgusting for many people. But if you take a closer look at the crustaceans, you will discover an interesting way of life. They do not necessarily have to be fought. There are certain reasons why the supposed pests appear in the house.

How can woodlice be controlled?
The prehistoric crabs can be fought using simple means, so you don't have to resort to poison straight away. Consider whether you really need to kill the animals. In the rarest of cases, woodlice become a nuisance, so you can get the woodlice out of the house using gentle measures.
Diatomaceous earth

Diatomaceous flour is an effective, natural remedy against woodlice
If you want to destroy woodlice without chemical agents, diatom meal proves to be effective. The powder, which is made from fossil diatoms, is as fine as dust and consists of sharp-edged crystals with a large surface area. It is harmless to users and is used to destroy numerous arthropods.
Application:
- apply into cracks and crevices
- Sprinkle heavily trafficked areas
- distribute within the radius of a lure
The fine crystals block the breathing openings that are distributed over the body. This means the woodlice can no longer breathe and suffocate. With regular and direct use, woodlice should no longer be a problem within four days.
Use beneficial insects
Nematodes of the type Steinernema carpocapsae have been used successfully for some time to combat woodlice. The nematodes themselves are not mobile, which is why they are used in the form of traps. The trap contains an attractant that attracts the woodlice. Upon contact, the nematodes penetrate the woodlice, where they secrete bacteria. These decompose the arthropod from the inside. Such traps only work at temperatures above twelve degrees, as the activity of the nematodes stops under these conditions.
Effective home remedies
You can use simple methods to capture or scare away the animals. Attractants work even better if you have eliminated the cause of the woodlice infestation. Then the crustaceans only find optimal living conditions in the area of the trap. Tackling the causes is the only solution to permanently get rid of woodlice. An occurrence always indicates suboptimal conditions in the house.
Potato as bait
When cooked, the root vegetables are a real treat for woodlice. Rotten potatoes are attractive and can be used as an attractant. Place the tuber on a plate and place a crumpled, damp cloth next to the ground.
Place the plate in the affected room and wait. The animals eat the food and then retreat to the damp hiding place. The next day, take the entire plate outside so that the crayfish can escape.
Wet wipes
If you don't have potatoes on hand, two large cloths will suffice as a trap. Dampen the fabric and spread a cloth on the floor. Drape the second piece of fabric in folds onto the surface and keep it moist with a spray bottle for the next few days. The woodlice will discover the new hiding place for themselves. Lift the bottom cloth and gather it into a sack to take outside.
Alcohol
Put a shot of high-proof alcohol such as spirits in a bottle and place it on the bottom. Insert a small piece of wood into the opening so that the woodlice can crawl into the bottle. They are attracted to alcoholic vapors and remain trapped in the bottle. To save the animals, you should check the trap regularly and remove woodlice.
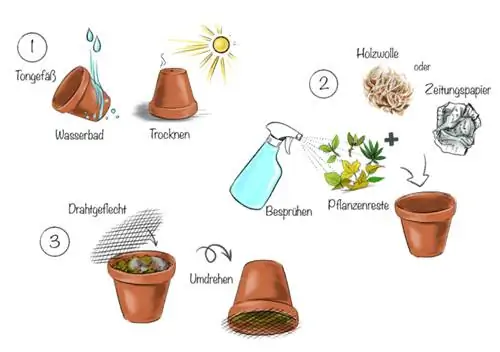
Claypot Trap
Soak a clay pot in a water bath so that the pores are completely saturated with water. Then let the pot drain well and dry the container. Fill it with wood shavings or crumpled newspaper and spray the material lightly with water.
You can also add plant debris to the clay pot to increase the attractiveness of the trap. Place a coarse-mesh wire mesh over the pot to hold the material inside well. Turn the pot over and place it in the room infested with woodlice. You should check the trap regularly for hermits and release them outdoors.
Essential oils
The aromas of various aromatic plants and herbs have a repellent effect on numerous pests and woodlice. By laying out fresh herbs or spices, you create a barrier that prevents or restricts access to rooms. The obstacle should be five centimeters wide and should be replaced regularly, otherwise the volatile aromas will have no effect.
Deterrent substances:
- Baking powder
- Cinnamon
- Sage
Prevention
If woodlice appears in the house, it is a sign that the humidity is too high. The arthropods have remains of former gills because they evolved from aquatic creatures. It prefers a humidity of at least 70 percent. If the animal is in the bathroom, basement or garage, you should find out the cause of the excessive humidity.
This increases the humidity:
- Water damage from pipes in the wall
- leaking basement walls that allow moisture to move inside
- moisture rising from the ground
- Drying rack with damp laundry
- Dryers that are used without a water collector
- organic waste or vegetable and fruit supplies
If you want to get rid of woodlice permanently, you need to eliminate the cause of their activity. Make sure that the arthropods cannot gain access to the interior spaces. Seal possible entry points with filler, silicone or clay. This also applies to cracks and gaps on windows or doors.
As a crustacean, the woodlice needs moisture. Dry air kills it.
Air properly

Proper ventilation is important to keep woodlice away
Regular ventilation reduces the humidity. At the beginning, open windows and doors when the outside temperature is as cool as possible. A burst of ventilation for five to ten minutes is sufficient to prevent the house from cooling down completely. If the humidity has decreased, airing it out daily in the morning or evening for 15 minutes is sufficient.
Storage technology for fruit and vegetables
If possible, store potatoes and other supplies in hanging nets. This ensures good ventilation and woodlice don't get to the food so easily. Alternatively, you can store vegetables and fruits in well-ventilated boxes. Damaged or overripe fruits and tubers should be removed as they are particularly attractive to woodlice.
Checking potted plants
Woodlice often come into the apartment with plants that are taken to their wintering quarters. If the soil feels moist and smells musty, the crustaceans feel comfortable in the substrate. Allow the soil to dry thoroughly before bringing the bucket in. To be on the safe side, you should lift the root ball out of the pot and check the substrate for hidden passengers.
Are woodlice useful or harmful?
Crustaceans are among the useful creatures that pose no danger to humans. In rare cases, the woodlice is a pest because it can view stored vegetables as food. When it eats its way through root vegetables, mold spores can settle in the feeding ducts and the food rots. However, this behavior is the exception. Woodlice are among the beneficial insects and take on important tasks in the ecosystem.

Benefit
Cellar woodlice are among the decomposers that decompose organic material and thus keep nature pure. They break down and digest dead parts of plants. During their two-year lifespan, the arthropods produce a lot of humus. The bound nutrients are released and can be used by plants. In this way, the crustacean completes nature's nutrient cycle. Woodlice in the compost are extremely effective decomposers that accelerate the breakdown of kitchen waste. They are also on the menu of numerous wild animals:
- Shrews
- Hedgehog
- Spiders
- Birds
Edible
Islice are rich in calcium, which they contain up to 40 times more than other insects. They convert the nutrient and store it in the exoskeleton and bones, improving their stability. This is why the creepy crawlies are also popular with survival experts, who use the easy-to-catch woodlice as emergency food. They are almost tasteless and can be eaten raw or roasted.
Where do woodlice live?
Cellar woodlice depend on high humidity, which is at least 70 percent. Their eggs and larvae die if the air is too dry and adult woodlice find it difficult to breathe and dry out. Therefore, the arthropods hide in damp niches or in the apartment during the day:
- in the house: feel comfortable in damp basements in rooms with high humidity
- in raised beds: moist soil under dense vegetation provides optimal living conditions
- in the garden: Stones or flower pots are ideal hiding places
The animals' natural habitat is the litter layer that forms in the forest or under bushes. Woodlice live in the area around their food and can therefore be found in decaying plant remains or rotten wood that is covered in fungal mycelia. Between 50 and 200 woodlice live in an area of one square meter. They crawl tirelessly in and on the ground and can reach a depth of 30 centimeters.
Excursus
When a woodlouse curls up
The woodlice is not one of the species that curls up. This behavior is exhibited by the woodlouse, which protects itself from danger. When curled up, the animals are able to survive even in drier habitats. Rolling up protects against excessive water loss. In addition, their respiratory organs on their hind legs are better developed than those of woodlice, which is also an adaptation to drier habitats.
Retreat Basement
In modern cellars, the humidity is usually so low that woodlice do not find optimal living conditions there. They can become a problem in old cellar vaults that are affected by rising and penetrating damp. Stored supplies provide the crawling creatures with optimal food resources.
Due to its sociability, a woodlice rarely comes alone. They gather in small groups within a few minutes and merge into a kind of nest, which dissolves if disturbed. Therefore, examine all niches in the area around the found animal.
Kitchen and bathroom
Basement woodlice rarely occurs in the bedroom or living room. However, they often occur in the bathroom because the humidity is slightly higher here. In the kitchen, woodlice are attracted to dog or cat food left open in the bowl. They retreat into gaps between wooden floorboards where the humidity is increased. The crustaceans often get into the living area from the basement. Optimal entry points are gaps around heating pipes that lead through the masonry into the basement.
Prevention tips:
- Place flower pots on pot feet or gravel to prevent moisture from forming under the ground
- Air the bathroom after showering and do not store wet towels on the floor
- Dry laundry in well-ventilated rooms
- ventilate in winter so that the masonry does not get damp
What do woodlice eat?
The diet of arthropods is mainly limited to dead organic substances. Live plants are usually not on the diet of woodlice. Occasionally they eat potatoes that are ready to be harvested or feed on stored fruits and vegetables. Woodlice don't waste any nutrients and therefore eat their own droppings.
Tip
You can easily tell that a woodlice has eaten your potatoes. The nodule has only one hole, which served as an entrance and exit. It is about three millimeters in diameter.
The woodlice in the profile
Woodlouse have 14 legs and a tail plate that is equipped with tactile organs. The name woodlice comes from the Latin term asellus, which is translated as donkey. They have the scientific name Porcellio scaber.
| Porcellio | scaber | |
|---|---|---|
| latin | porcellus, -i | scaber, -bra, -brum |
| German | Piggy | rough, mangy, unclean, shabby |
Cellar woodlice belong to the land isopods and are characterized by an unmistakable body structure. Their carapace has the shape of a half ring and is finely serrated. This has a slate to yellow-gray color. The animals are rarely colored red and spotted black.
Reproduction
The courtship behavior of woodlice begins with a waving of the antennae. The male then crawls onto the female's back and assumes a diagonal position in order to reach the female's genital opening. They have two of them on each side. After fertilization, a female carries between 25 and 90 eggs on her body. With this high reproduction rate, the crustaceans make up for their losses from enemies.
Development

Red woodlice shed their skin around 15 times before they reach sexual maturity
The eggs remain in a fluid-filled sac on the female's stomach for the next 40 to 50 days, even after the larvae have already hatched. These molt 14 to 16 times before they reach sexual maturity. It takes about three months for a baby woodlice to become an adult. Additional molts occasionally occur during their two-year life:
- Moulting happens when calcium stores on the underside of the abdomen are full
- first the bottom sheds its skin
- Finally the head sheds its old skin
Interesting facts and special features
The woodlice is not an insect but is a crustacean. In its family group, it is the only species that has been able to adapt to a permanent land life. There are a total of around 3,500 different species of isopods, which look back on an evolution that goes back far into the past. The oldest finds of fossil woodlice are 50 million years old. Many isopods probably developed around 160 million years ago, when the continents were still connected. Today the families of land isopods can be found worldwide.
This is what distinguishes woodlice from insects:
- do not have a protective wax layer
- have gill-like breathing openings
Immune system
The prehistoric crayfish have an interesting immune system that is reminiscent of that of humans. It is able to detect bacteria. If the animals have previously come into contact with certain bacteria, the immune system recognizes these organisms and decides how to proceed. If there is a risk of illness, immune activity is increased. This process is normal for the human immune system. The simply knitted crustaceans are a special feature.
Metal detector
Cellar woodlice are able to absorb metals and store them in small fat globules. The higher the concentration in the soil, the more the animals store. This has a positive effect on their height. Woodlice that live in soils with high metal concentrations grow larger. That's why people use woodlice as metal detectors.
Ammonia excretion
The land crabs are crossed by a water system. Since woodlice do not produce urine, they have to remove the resulting ammonia from the body in another way. This happens via the circulating body fluid. Ammonia is released into the air via the surface of the body through evaporation. This ability ensures the animals' life on land because they would lose too much fluid through urine production. The ammonia-free liquid is then used to moisten the gills.
Breathing
In the course of their evolution, woodlice have developed tracheal lungs, which are located on their hind legs. They have additional gills that allow the animals to absorb oxygen from the air through the surface of their bodies. However, these gills are greatly reduced and only function in exceptional cases. Woodlice absorb most of the oxygen through their tracheal lungs.
Tip
Turn the woodlice on its back and look at the underside. You can clearly see the tracheal lungs because they are colored white because of the air filling.
Frequently asked questions
Can you breed woodlice?

Breeding woodlice is very easy
Islice are ideal for breeding because they do not require much attention. Only the living conditions should be optimal so that the animal feels comfortable. There are different types available to buy commercially, as these are preferably fed to farmed amphibians or reptiles.
Common feeding and breeding isopods:
- Cuban woodlice: Porcellionides pruinosus
- Giant woodlice: Porcellio hoffmannseggi
- Black and yellow woodlice: Porcellio haasi
The University of Münster is the founder of a isopod workshop and provides detailed information on keeping land crabs. There are a number of experiments here that invite you to explore the woodlice.
What enemies do woodlice have?
The line of predators is long. The large woodlice hunter is a species of spider that specializes in woodlice. Woodlice flies produce larvae that are parasitic and feed on the hemolymph and organs of the woodlice. They spare vital organs until the end in order to be able to use them as much as possible. They then pupate in the crustacean and leave the dead body as an adult fly.
Insectivores such as hedgehogs, shrews, frogs and toads also feed on woodlice. They occasionally fall prey to little owls, slowworms and even ground beetles, harvestmen or centipedes. Iridovirus is a fatal disease that causes infected woodlice to turn blue or purple.
Where do woodlice come from?
Cellar woodlice originally come from Western Europe and the Atlantic region. They were spread worldwide by humans. They feel comfortable in human surroundings. The woodlice is often found in damp basements, which is where it got its German name. In Central Europe, the woodlice is considered the most common and widespread species among the land isopods. It lives mainly in the litter layer of forests with medium-humid conditions. Woodlice are typical in stables, greenhouses or in the compost.
Are there several species of woodlice?
The woodlice is an independent species with the scientific name Porcellio scaber. There are other species that occur in similar habitats and are also common in gardens and basements. This includes the wall woodlice Oniscus asellus, which requires slightly higher humidity than the woodlice. In contrast to the woodlice, this species has a rather smooth shell.
The Common Woodlice Armadillidium vulgare is another species native to Europe that occurs mainly in the Mediterranean region. The supposed giant isopod from the sea is Bathynomus giganteus, which belongs to the genus of giant isopods.
How can woodlice be effectively attracted?
Since the crustaceans prefer to feed on dead plant material, you can use old vegetables for bait. Overripe or already rotten carrots and potatoes are particularly attractive to the animals. While they feed on the attractants, they can be easily caught and released outside. Arrange the root vegetables on a plate for the useful helpers. This can then simply be lifted and taken outside without the woodlice escaping.






