- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-24 06:09.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
The natives of South America already knew about guano as a fertilizer 500 years ago and diligently fertilized their fields with it. In the 19th century, “white gold” was a sought-after commodity as this natural fertilizer contains very high levels of the essential plant nutrients phosphorus and nitrogen.

What is guano?
The word guano comes from the Andean language Quechua, which refers to the origin of this once highly competitive fertilizer. Translated it means “dung”, because it is nothing else. Guano is the excrement of seabirds - mostly the remains of penguins - which contains an immensely high proportion of nitrogen and phosphorus as well as many trace elements and is therefore ideal for the natural fertilization of garden and house plants. However, the organic fertilizer is not for everyone as it has a pungent and unpleasant smell.
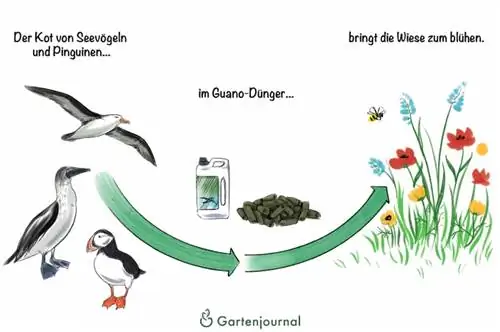
Ingredients and uses in the garden
Guano fertilizer provides the soil and thus the plants growing on it with a balanced mix of nutrients, as the material contains phosphorus and nitrogen as well
- many enzymes
- Minerals
- Trace elements
- Proteins
- and beneficial bacteria.
The specific proportion of the respective nutrients varies greatly and depends on various factors, such as the mining area and the diet of the seabirds. The subsoil and the age of the mining site are also important for the ingredients, because over time the bird droppings mix with the calcareous rock underneath. After all, it is an organic product which, like all organic fertilizers, is subject to fluctuations in its composition.
The types of guano fertilizers
Guano fertilizers are commercially available in various forms and compositions. Pure guano is rarely sold; manufacturers usually offer synthetic or organic NPK fertilizer with certain proportions of guano. How high this proportion is varies from manufacturer to manufacturer and can range from a minimum percentage to 70 percent.
Guano fertilizers are also available in different forms:
- Powder
- Granules or pellets
- Liquid fertilizer
- Fertilizer sticks
Guano in powder or other solid form is best applied directly to the soil and lightly incorporated. Then don't forget to water so that the fertilizer gets deeper into the soil and closer to the roots. However, you can also dissolve these solid guano fertilizers in water and then use them as foliar fertilizer. To do this, simply spray the product onto the plant foliage. Due to the unpleasant smell, you should only use special fertilizer sticks or appropriately labeled liquid fertilizers for houseplants.
Excursus
What is bat guano?
Not only seabirds - and penguins in particular - produce guano diligently, other animal species are also responsible for this. Special bat guano is available for the garden, also known as bat guano, which contains on average slightly less nitrogen but more phosphorus than the remains of seabirds. However, this fertilizer is problematic because to obtain it you have to visit bat roosts that are often difficult to access and disturb the animals to break down their droppings. This is not the only reason why bat guano is very expensive: a kilogram of such fertilizer costs between 12 and 25 EUR, depending on the manufacturer.
Areas of application and possible applications

Guano is not only suitable for fertilizing garden, pot and house plants, but is also used for other purposes in the garden bed:
- Stimulation of soil organisms: Thanks to the enzymes and bacteria it contains, guano ensures improved soil life, so that when applied, the composition of the soil structure changes - but only very slowly.
- Improving soil quality: With regular guano fertilization, both the texture and drainage of the soil improve over time, which is due to the increased activity of soil organisms.
- Fungicide: In addition, a highly concentrated guano fertilizer can also be used as a fungicide, for example by combating or preventing fungal diseases - which often occur on many garden plants - through foliar fertilization.
- Compost Activator: Due to its ingredients, guano is also very suitable as a compost activator and as such accelerates the decomposition process in the compost heap. The result is high-quality compost soil.
Which types of fertilizer contain guano?
You can literally make gold out of bird droppings.
Commercial guano fertilizer only rarely consists of pure or even highly concentrated guano. Most manufacturers use bird droppings as part of an NPK fertilizer, which also contains other ingredients of either organic or synthetic origin. The proportion of guano is not always specified, but it rarely contains more than 30 percent of the material.
| Medium | Manufacturer | Area of application | Application form | Price | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flower fertilizer with guano | Compo | for indoor, balcony and other potted plants | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 4.80 EUR / liter | contains synthetic ingredients |
| Flower fertilizer with guano extract | Dehner | for flowering plants in the garden and pots | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 4 EUR / liter | contains synthetic ingredients |
| organic garden fertilizer with guano | myorganicgarden | Garden fertilizer for vegetables, herbs and fruit trees | Granules | approx. 5 EUR / kilogram | approved for organic gardening |
| BIO natural fertilizer with guano | Compo | for all garden and vegetable plants, fruit trees | Granules | approx. 5 EUR / kilogram | approved for organic gardening |
| Flower fertilizer with seabird guano | Gärtner’s | for flowering plants in the garden and pots | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 8.30 EUR / liter | also suitable for green houseplants |
| Plant food with guano | Substral | for green and flowering potted and container plants | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 4, 60 / liter | also suitable for houseplants |
| Balcony and pot plant food with guano | Substral | for green and flowering potted and container plants | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 5.30 EUR / liter | also suitable for houseplants |
| Fertilizer sticks plus guano | Compo | various varieties for green, flowering and potted plants | Fertilizer sticks | approx. 2, 70 / 30 pieces | Long-term fertilizer |
| Flower fertilizer for home and garden with guano | Biplantol | for ornamental plants | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 9.80 EUR / liter | with homeopathic complex |
| Quick composter with guano | Compo | for composting | Granules | approx. 4.30 EUR / kilogram | Composting aid |
| Guano fertilizer for rooms, balconies & terraces | Chrystal | for potted plants | Liquid fertilizer | approx. 8.90 EUR / liter | NPK fertilizer |
Tip
Caution: Not everywhere that says “guano” necessarily has guano in it. Cheap products in particular contain either very small amounts or even just chicken or other bird droppings. Here, however, the nutrients are composed completely differently, because it is the fish-rich diet of seabirds that makes this natural fertilizer unique.
How to use guano correctly in the garden
The use of guano fertilizer depends primarily on the form in which you use this fertilizer. Work solid guano directly into the soil, ideally at a depth of around seven to ten centimeters, and then water thoroughly. You can also add the fertilizer into the planting hole directly when planting. Make sure that no fertilizer remains stick to the leaves, as this can cause chemical burns and thus leaf damage.
Guano is in liquid form, but is no longer corrosive and can therefore be used both for direct watering onto the soil and for foliar fertilization. Mix the liquid fertilizer with the irrigation water according to the package instructions and apply both to the plants immediately.

Guano is also available in stick form for houseplants
For indoor and other potted plants, however, fertilizer sticks are suitable, which you simply stick individually into the soil at the edge of the plant pot - but at a distance of about one to two centimeters from it. In the coming weeks, the stick continuously releases nutrients to the plant, so you no longer have to fertilize.
Like all fertilizers, guano is best used during the growing season between March and September. With the exception of pure houseplants, garden and balcony plants are in a resting phase from this time on and therefore do not require any fertilizers.
Dosage
Since the specific ingredients of the different guano fertilizers vary greatly, of course no concrete statements can be made here. It is best to pay attention to the relevant information on the product packaging. However, some general statements regarding dosage can be made:
- Guano fertilizer can be dosed sparingly.
- Count on 40 to 80 grams of guano per square meter of garden area.
- Fertilize with this amount once in spring at the start of the season.
- If necessary, repeat this fertilization in June, but no later than the beginning of July.
Dilute liquid fertilizer with guano with the irrigation water, shaking the bottle vigorously before use. This is necessary so that the grounds stuck to the bottom are released and remixed with the remaining liquid in the bottle. Dosing is very easy with most liquid fertilizers, as you can simply measure the amount required using the bottle cap.
Fertilization is best done weekly during the growing season, although you should base the amount of nutrients on the actual needs of your plants. After all, some species need more food than others, which get by with significantly less.
Excursus
Disadvantages of Guano
The nutrient cocktail made from guano fertilizers decomposes very slowly, and the granules in particular require active support from soil-dwelling microorganisms. For this reason, the effectiveness of these fertilizers may be low in hot and dry summers and low on some soils. Furthermore, some types of fertilizer release unpleasant odors.
Make your own liquid guano fertilizer

If you have solid guano at home, you can easily make liquid fertilizer yourself
If you have pure guano at home, you can use it to make individually dosed liquid fertilizers. How much of the material you actually need per liter of water and per square meter of planting area depends largely on the specific composition of the product and your soil. On average, you use between 40 and 80 grams of guano per square meter of soil, which also shows how little of the fertilizer you actually need compared to other organic fertilizers such as manure or compost. And this is how you make the liquid fertilizers:
- Guano tea: Dissolve about one to two tablespoons of guano in five liters of water, let the mixture stand overnight and water your plants with it the next morning.
- Guano brew: Here you let the guano tea stand for about 24 hours so that the mixture bubbles and thus indicates fermenting activity. Pour the broth directly onto the soil area below the plants. Not only do the plants themselves benefit, but also the organisms and useful animals in the soil.
Use these two products only in the fresh air, i.e. in the garden. Home-made liquid fertilizers are not suitable for fertilizing indoor and other potted plants as well as greenhouse plants due to their pungent smell.
Origin and occurrence
It's not just seabirds that are responsible for the huge guano deposits, primarily in South America, various mammals that live there, such as seals, also contribute with their remains. Furthermore, the deposits also contain the eggshells as well as carcasses and bones of these birds and over time have piled up into mounds several meters high - some of these mounds are up to 30 meters or more high.
Most of the deposits are on the islands off Peru, which Alexander von Humboldt visited at the beginning of the 19th century and brought the first samples from there to Europe. There are also deposits in Egypt and India. Nowadays, however, not only natural deposits are being mined more and more frequently, but artificial “guano islands” are also being created. To do this, various tricks are used to attract seabirds to these platforms floating on the sea, which then leave their valuable droppings there. According to scientific calculations, the approximately one billion seabirds on earth produce around 600,000 tons of nitrogen and 100,000 tons of phosphorus - per year. Only the quantities that the birds defecate on land are included here - the occurrence in the sea is not taken into account.
The mining sites for bat droppings, on the other hand, are largely located in Europe.
Excursus
Influence of guano on the climate
Did you know that the guano deposits of the Humboldt penguins living at the southern tip of South America have a major influence on the climate of the Antarctic region? In fact, the deposits are so large that the escaping ammonia rises into the atmosphere, where it contributes to cloud formation and thus to cooler temperatures.
Guano - ecologically questionable

The Humboldt penguins rely on guano
As positive as all of these descriptions of guano sound and as much as the manufacturers praise the material as organic, the breakdown of bird droppings is ecologically questionable. It's not just the fact that the raw material for guano fertilizer comes to us from practically the other side of the world that should be a cause for concern: the transport of the product on this journey causes large amounts of climate-damaging CO2, even though we have enough, equally valuable fertilizer with us have at home.
But the Humboldt penguins also suffer from the degradation of their guano sites, because the animals dig their breeding burrows into these hills as protection from the cold and other adverse weather conditions. However, if the guano deposits disappear, the penguin will no longer find any opportunities to nest. The result is that populations have declined sharply since mining began.
Alternatives to guano
Instead, you can rely on numerous local and no less beneficial organic fertilizers that do not pollute nature or ecosystems. In addition to the obligatory compost and manure from horses and cattle, it also includes nettle and other plant manure, as well as composted chicken manure as a kind of local substitute for guano. Chicken guano is also rich in nutrients and minerals and can be made yourself using this recipe:
- Collect fresh chicken manure.
- Place this in a compost bin.
- Water the manure thoroughly.
- Mix bedding (mainly finely chopped straw) into it.
- Turn the mixture thoroughly every few weeks.
- The chicken manure will be composted after about six to twelve months.
- It can now be used as fertilizer in the garden.
Frequently asked questions
Is guano poisonous? What do I do if I accidentally swallowed the fertilizer?
Rest assured: Guano is not poisonous, but can only have a slightly corrosive effect on the mucous membranes and respiratory organs. If you have inhaled or swallowed some of the dust, get some fresh air and breathe deeply. It also helps to drink lots of water and practically flush yourself. However, if something gets on your skin, wash it off with soap and water; if it comes into contact with your eyes, rinse out the residue with clear water. A visit to the doctor is only necessary if you feel unwell afterwards.
Doesn’t guano fertilizer smell terrible?
Guano fertilizer actually smells quite pungent, but this is not noticeable when used in the fresh air.
Is guano also suitable as a long-term fertilizer?
Guano is very suitable as a long-term fertilizer, as the nutrients are only released very slowly anyway. For example, when planting, you can add about a tablespoon of the powder per plant into the planting hole so that your plants are well looked after right from the start.
Is guano fertilizer also suitable for orchids?
Some liquid guano fertilizers that are sold specifically for house and balcony plants are also suitable for orchids. As a rule, a dosage recommendation is stated on the packaging.
Can I also use fresh chicken manure for fertilization?
Unfortunately, fresh chicken manure is not suitable as fertilizer because it is too corrosive and would practically kill the plants. There is also a risk that using fresh manure will transmit pathogens such as salmonella to the plants and enter your body through them. For this reason, composted chicken manure should also be added to the soil some time before the plants are planted. The same applies to other bird droppings, such as those produced when keeping pigeons. However, you should not use duck and goose droppings, as both types often permanently excrete salmonella.
Tip
Because guano has a corrosive effect, you should always wear gloves when applying this fertilizer. In addition, the dust should not get into the respiratory tract or eyes. Also avoid dusting the above-ground parts of the plant with guano dust, as contact causes burns. It is therefore best to always fertilize on a calm day!






