- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:20.
With each growing season, the resilient blood plum produces new shoots and seeds. However, these do not always lead to the desired habitus. Find out more about the professional finishing process.

How to successfully propagate blood plums?
Blood plums can be propagated by seeds or shoots, but these plants will not bloom without professional grafting. Shoots should be removed regularly to ensure water and nutrient supply.
Propagation the natural way
Seeds
The easy-care ornamental tree produces a variety of fruits in an ideal location. The seeds are not suitable for consumption, but they are used for propagation.
Shoots
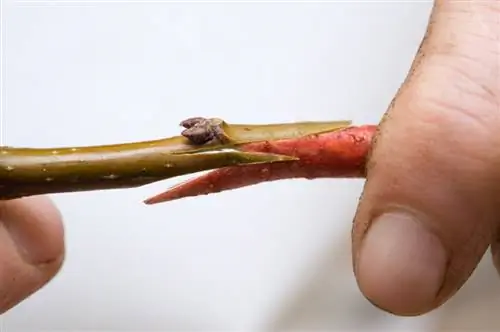
In addition, you can always see new shoots on these rose plants. Small plants can be grown from these. To do this, these young shoots are cut off at a slight angle after harvesting. The cuttings overwinter in the ground in a frost-protected garden house or alternatively in a greenhouse. They are already starting to form roots. You can plant these in the garden in spring (April to May).
Note:
Blood plums grown from seeds or shoots will not bloom. Refining by a specialist is necessary.
Attention: wild shoots
However, as they grow larger and older, wild shoots deprive large trees of valuable nutrients. They also hinder the unrestricted incidence of light and the supply of water. Since these shoots are difficult to remove from the ground when they reach a certain size, the following tips are useful:
- Remove shoots regularly
- cut directly on the trunk (smooth cut)
- or carefully pull it out of the ground
Refining: A short digression
This complex method is used to propagate all fruit trees. The gardener grafts young plants between June and August. In most cases, the specialist market offers blood plums that have been grafted onto the trunk. The Prunus cerasifera Nigra is one of the preferred varieties.
You will almost exclusively find shallow-rooted plants. These are blood plums that have been grafted onto sweet wild plums. Alternatively, the offer also includes specimens refined on trunk.
Tips & Tricks
The small shoots on the side of the trunk differ significantly from the mother plant. These are not used to grow new trees. If you remove these, a sufficient supply of water and nutrients is guaranteed.