- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
Moles are remarkable animals with enormous productivity. Many garden owners experience this in their own garden when the animal produces mass piles of earth on the area. But the hills don't necessarily have to be equated with the gardeners' suffering.

What can you do about molehills?
To remove molehills, moles should be discouraged and not killed, as they are protected. Annoying noises, smells or obstacles can be effective methods to rid the garden of moles and then eliminate the mounds.
What to do about molehills?
Before you remove the molehill, you should identify and get rid of the culprit. With all measures you have to consider whether they really make sense. Otherwise you can quickly come into conflict with the nature conservation law. Therefore, do not use any chemical agents, but instead use gentle home remedies.
Fighting forbidden

The mole is protected in Germany and may not be killed
In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, the mole is listed as a specially protected species according to the Species Protection Ordinance. According to the Federal Nature Conservation Act, it is forbidden to kill, capture or injure specially protected species. Anyone who violates the law risks high five-figure fines.
Remedies for molehills
To get rid of molehills, you have to scare away the mole. Simply removing the molehills further exacerbates the problem as the animals speed up their digging activity. There are some home remedies that effectively get rid of moles. In order to be successful, the funds must be distributed at regular intervals of a few meters in the underground passages. Provide the mole with an escape route so that it can leave the garden.
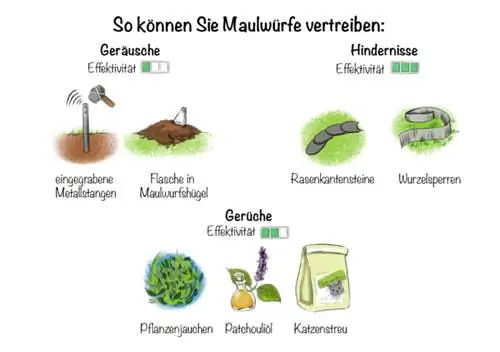
| Medium | Application | Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sounds | buried metal bars | frequent knocking with a stone | less promising |
| Smells | Plant manure, patchouli oil, cat litter | incorporate evenly into corridors and hills | effective when renewed regularly |
| Obstacles | Lawn edge stones, root barriers | lay in the ground in front of the bed and lawn | successful prevention |
Bottles in molehills
Empty bottles that are buried directly in the molehill and in the tunnels are said to disturb the animals. The neck of the bottle protrudes about ten centimeters from the earth, so that the wind creates sounds as it flows in and out. These noises spread underground in the corridors. For the method to be effective, the bottles must be distributed over the entire area. Otherwise, the mole will quickly find alternative options where it will not be disturbed.
´Moles have sensitive senses. They are sensitive to disturbing noises and smells.
Leveling molehills - caution is advised

Leveling molehills is not very effective
The molehills are not just accumulations of excess earth material. They serve as vital ventilation systems so that the mole gets enough oxygen in its underground burrow. The animal produces a lot of carbon dioxide, which accumulates in the burrows. If you level a molehill, the mole will quickly dig new ventilation holes. In this way he avoids the danger of suffocation. As a garden owner, you should take other measures.
If the mole disappeared:
- Remove soil and use as potting soil for demanding plants
- Distribute the pile with a rake so that surrounding vegetation gets fresh soil
- Wash away hill with garden hose
- Press the pile and flatten it
Removing molehills with the lawnmower?
The mounds of earth can be easily distributed with the lawnmower and, in the best case, the earth ends up in the grass catcher with the grass clippings. But caution is extremely important with this measure. When moles push the earth up, small stones can also get into the molehill. These are not immediately visible and cause damage to the knives.
How do molehills form?
A mole in the garden does not meet with goodwill from most hobby gardeners. Molehills are not welcome in beds or on the lawn. The mammals are able to pile up up to 20 mounds of earth per day. Their digging activity underground can loosen or damage plant roots. However, the mole is not a plant pest because it feeds exclusively on animal prey.

Digging activity
Moles dig with their forelimbs, which are converted into digging tools. The outwardly turned palm pushes away the substrate that has been loosened by the five toes. As the soil piles up, the mole pushes the material to the surface of the soil with its head. Depending on the nature of the soil, this is done at a distance of 50 to 100 centimeters. The animals push the earth upwards to the side so that the molehill is created at an angle above the passage.
Why gardeners benefit from moles:
- Substrate is loosened and ventilated over a large area
- Fine crumbly excavation is ideal as growing soil.
- Moles eat pests
Tip
Lawnmower robots are intended to drive away moles because the animals react sensitively to the continuous noises and vibrations.
Molehills in winter

Moles continue to dig diligently even in winter
Moles are also active in winter because they do not hibernate. During the winter months it is more common for the animals to create a so-called mole castle. This consists of a central hill that is significantly larger than the piles of earth surrounding it. The mole builds his nest under the castle.
When the weather is particularly wet, the upper layers of soil become softened, meaning that worms and insects increase. Moles forage for food close to the surface and produce more excavation than in drier times. In this weather, the mole moves its nest and creates an above-ground swamp castle.
Excursus
Farming rules around the molehill
Animals have a special meaning in farming rules because weather forecasts can be made based on their behavior. The saying “If the molehills are high in the garden, a harsh winter is to be expected” refers to the typical mole castle that the animals build in the winter months.
The farmer's rule “If the moles dig deep, it will be a hard winter” can be interpreted in the same way: in severe winter months, the ground frost moves into deeper layers of the earth, so that moles have to retreat further into the ground.
Identifying molehills
It's not just to satisfy your interests if you find out who is causing the mounds in the lawn and bed. Identification is the first step to taking action. Since the mole is a protected species, careless control methods can result in high fines.
Vole hill - difference from molehill
Vole mounds are often attributed to the digging activity of moles. At first glance, the piles of earth from both garden inhabitants look very similar. Pay attention to whether there are plant remains and roots in the piled soil. Such remains indicate the activity of voles that feed on plants. Molehills are free of plant residues.
- Tube cross-section: transverse oval in the mole, high oval in the vole
- Mound shape: rounded in the mole, elongated and flatter in the vole
- Tunnel system: Voles dig directly under the turf, moles dig in deeper layers of earth
Crush test
The rummaging test gives you a clue to the culprit. Insert a stick into the ground in a circle around the mound to feel it. If you encounter a cavity directly beneath the turf, a vole is most likely responsible for the mounds. To confirm this suspicion, open a section of the duct system over a length of 30 centimeters. Be careful so that the tunnel does not collapse.
Since voles are very active, they will close the hole again within the next few hours. Moles take their time with the repair work. They appear fearful and perceive the destruction as a threat. Only in rare cases do moles close the duct opening. They usually avoid the open tunnel and dig an alternative passage.
Tip
Wear gloves when doing this because the vole can also be influenced. She perceives human body odor as a threat.
Frequently asked questions
How do moles survive the winter?

Moles stock up on worms for the winter
The animals create an underground food supply consisting of live worms. The mole bites off the front body segments of the invertebrates so that they continue to live and can no longer escape. If the earthworms do not survive this type of storage, the mole will no longer touch them.
How deep does the mole dig?
The tunnel systems are not located directly under the turf but at a depth of between ten and 20 centimeters. If the conditions in this area are not optimal, the animal will retreat to deeper layers of soil. Its tunnel system, which can be up to 200 meters long, often extends to a depth of up to one meter.
Do molehills have an ecological purpose?
The digging activity of the animals indicates he althy soil. The more hills there are on an area, the more species-rich the soil life is. The mole proves to be a natural pest controller, controlling the populations of various insects. Through its passages it ensures soil loosening and drainage. The hills ensure an optimal growth base for plants that cannot gain a foothold on a closed vegetation cover.
Do moles have specific activity times?
Since the animals live underground, they do not follow a distinct day-night rhythm. The activity of the European mole is divided into three phases of sleep and wakefulness. The animals are active for around four to five hours in the morning, afternoon and around midnight. When they don't sleep, they dig more tunnels and hunt for prey. Their activity is all year round and is not interrupted in winter.






