- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
If you discover a black wasp in your garden, you don't have to be afraid. These insects have little in common with the dreaded wasps that harass the coffee table. There are numerous species that are black in color. Many species prove useful in the garden.

Are black wasps dangerous in the garden?
Black wasps in the garden are mostly harmless and useful insects that belong to the group of waist wasps or plant wasps. They can be digger wasps, parasitic wasps, wasps or stalk wasps and often live solitary lives without posing a threat to humans.
Black wasp discovered - what kind?
Wasps are various types of hymenoptera, which include 156,000 species worldwide. They belong to different orders and families that follow variable lifestyles. Waist wasps include not only German wasps, honey bees and wood ants, but also numerous inconspicuous species. Small black insects are also found among plant wasps.
| Waist wasps | Plant wasps | |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Body has a constriction | no noticeable wasp waist |
| related families | e.g. Wasps, parasitic wasps and grave wasps | e.g. stalk wasps |
| Lifestyle | predominantly parasitic | mainly herbivores or nectar eaters |
Identification tips

Digging wasps have small, often black wasps with a very fine body
Scientists do not make it easy for laypeople to identify a species of wasp discovered in the garden. Pictures and notes from the discovery site are important in order to be able to assign the species to a specific family. Each family is characterized by specific characteristics and different ways of life. The coloring is not a clear characteristic, which is why black colored wasps can be found in various families of waist wasps as well as plant wasps.
Exemplary system:
- Order: Hymenoptera
- Subordination: Waist wasps
- Partial order: Stechimmen
- Families: e.g. wasps, grave wasps, parasitic wasps
Take notes about where the wasp was found. The habitat provides informative information about the species, as many have specialized in certain biotopes. Images are necessary because the insects can only be identified based on their specific body characteristics. A photo is often not enough because fine details of the wasps usually remain hidden. Therefore, take as many pictures as possible and cover different perspectives.
Overview: common species
Most black wasp species are small to medium-sized and reach a body size of less than two centimeters. These wasps are classified as waist wasps or plant wasps. Larger species usually belong to other family groups. They can be observed in species-rich habitats and are often found close to humans.
Identifying black wasps requires knowledge of the characteristics of the numerous families.
Identify small black wasp
In Germany there are a large number of wasp species that are barely larger than one centimeter. Most species prefer open and sandy habitats as they build their nests in the substrate. A diverse vegetation offers the insects valuable refuge and protection during the winter. Dry and sandy garden areas such as gaps in walls or joints between paving stones are also colonized. Other species have specialized in wetter habitats such as meadows and forests, or colonize dead wood.
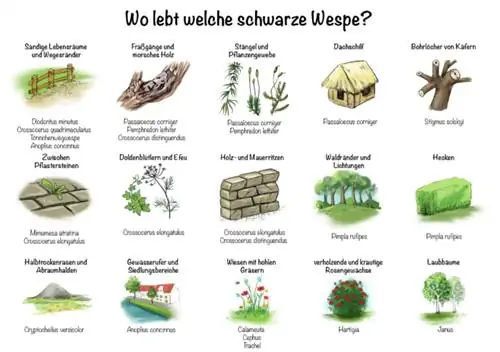
Digger wasps: Pemphredoninae
Within this subfamily there are numerous black colored species that are difficult to distinguish from one another. They inhabit similar habitats and are small to medium in size. This subfamily is one of the most developed digger wasps. Some species exhibit behavior similar to that of bees. The preferred habitats hardly differ between the common species that occur in human settlement areas:
- Diodontus minutus: prefers sandy habitats and roadsides
- Passaloecus corniger: adaptable, nests in feeding tunnels, pithy stems, plant tissue and roof reeds
- Pemphredon lethifer: nests in feeding tunnels, rotten wood, plant tissue or pithy stems
- Stigmus solskyi: uses abandoned boreholes of beetles
- Mimumesa atratina: likes to nest between paving stones
Digger wasps: Crossocerus
This genus includes around 200 species, 37 of which occur in Central Europe. These insects prefer cooler climates and are less common in the south. They are small to medium sized and often black in color. The fine point-like structure is typical, although the body also has smooth and shiny areas. An exact species identification is difficult because many species are very similar. The females build their nests in the ground or partly in wood and hollow plant stems.
Black colored species:
- Crossocerus elongatulus: on umbelliferous plants and ivy; nests between paving stones, in wood and cracks in walls
- Crossocerus distinguendus: common in various habitats, often in dead wood and cracks in walls
- Crossocerus quadrimaculatus: inhabits warm sandy habitats
Parasitic wasps
This family represents the most species-rich group of hymenoptera found in Central Europe. Parasitic wasp larvae live parasitically and feed on butterflies, beetles, plant wasps, spiders and other insects and their larvae. Their preferred habitats have humid conditions. They live in wet meadows or bushy parks.
The black parasitic wasp (Pimpla rufipes) can often be observed at the edges of forests and clearings or in hedges. It has a slender body that is ten to 15 millimeters long. Her body is black in color, with the light orange legs clearly standing out.
Weps
The species in this family are easy to distinguish from similar Hymenoptera in sunny and warm weather because they have a special way of life. Females actively crawl on vegetation or the ground to search for prey. They prefer prey with a similar lifestyle and predominantly hunt spiders. There are 100 species in Central Europe, of which these black colored wasps are more common:
- Cryptocheilus versicolor: rare in structurally rich habitats, on semi-dry grasslands and tailings heaps
- Tönnchen wasp: one of the most common wasps in residential areas, likes to live in sunny and warm places
- Anoplius concinnus: inhabits sandy habitats, water banks and settlement areas
stalk wasps

Stalk wasps only look vaguely similar to “real” wasps
Most species of these plant wasps are black, although there are also some with yellow markings. The graceful and elongated body is typical. Their abdomen is cylindrical in shape. They are between four and 18 millimeters long and have a movable head that is clearly separated from the body. 19 species have been described in Germany, one of which is extinct and another is considered lost.
| Genus | species native to Germany | habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Caenocephus | 1 | unknown, only found once in Brandenburg |
| Calameuta | 2 (another extinct) | Meadows with hollow grasses |
| Cephus | 7 | Meadows with hollow grasses |
| Hartigia | 3 | woody and herbaceous rose plants |
| Janus | 3 | Deciduous trees |
| Trachelus | 2 | Meadows with hollow grasses |
Big black wasp?
A supposed large black wasp in Germany is causing some observers to feel uneasy. The large carpenter bee (Xylocopa violacea) reaches a size of between 20 and 28 millimeters and is one of the largest bees in Central Europe. The deep black colored species with the bumblebee-like appearance is occasionally mistaken for a black hornet. The dark-toned wings, which have a blue shimmer, are striking. It is more common in warmer habitats.
Excursus
Megalara garuda - Asian giant wasp
The males of this still largely unknown species can grow up to six centimeters tall, while the females remain somewhat smaller. They belong to the digger wasps and are jet black in color. The mouthparts are longer than the forelimbs and are fearsome. Their shape is sickle-like. Females have a stinger that they can use to paralyze their prey. Californian scientist Lynn Kimsey discovered living specimens of this species on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi. It has not yet been observed in the wild.
Steel Blue Cricket Hunter
This digging wasp with the scientific name Isodontia mexicana reaches a size of up to two centimeters, with males being slightly smaller than females. They appear solid black and have blackish wings that shimmer bluish in the sun. Adult insects are flower visitors and are often observed on goldenrods or man litter.

Dangerous, harmless and useful species
Because the species spectrum of black wasps is so broad, the behaviors also differ between species. Therefore, there are both useful and harmful species. Black wasps usually do not pose a danger to humans.
Tip
Plant wasps are harmless. However, many species can harm your plants. Black wasp pests on grain belong to the stalk wasps. But there are also conspicuously colored pests such as the rapeseed sawfly.
Defensive behavior
Whether a black wasp can sting depends on the species. In principle, stinging insects, which include wasps and digger wasps, can be dangerous to humans. These species have a defensive spine with which they protect themselves against potential predators. If they feel threatened by humans, they may be bitten. This is more or less painful and heals on its own in most people. Sensitive people and allergy sufferers may experience symptoms similar to those of a wasp or bee sting.
Is a black wasp poisonous?
In the insect kingdom, species draw attention to their toxicity by developing warning colors. A typical example of this so-called aposematism is the German wasp with its characteristic black and yellow signal pattern. It alerts potential predators to its defensive capabilities.
Researchers from Granada have found that the amount of poison is linked to the luminosity of the warning colors. The more intense the yellow-black color of the collected wasps, the more poison these insects had in their stingers. Black wasps in Germany, on the other hand, are non-poisonous.
Harmless species

Parasitic wasps have a stinger, but they don't sting people with it
The legimen, which include parasitic wasps, have an ovipositor stinger. Females use it to inoculate their eggs into a suitable substrate. Like plant wasps, they cannot sting with this stinger. There are also species with an ovipositor among these hymenoptera. Female black wasps can look frightening with their ovipositor, as it protrudes significantly beyond the tip of their abdomen.
Useful
Numerous black wasps prove to be useful creatures in nature. Digger wasps feed on flower nectar and pollen. Their offspring are fed spiders and other insects. Some species lay their eggs in plant galls created by stalk flies. Wasps hunt spiders that have a similar lifestyle. Their diet includes funnel-web and orb spiders. They don't stop at crab or sac spiders and can kill the common house spider.
- Crossocerus larvae eat small flies, dust lice or psyllids
- Parasitic creatures prey on plant wasps, harmful beetles or moths
- Large carpenter bee pollinates mint plants, roughleaf plants, daisies and butterflies
Tip
To encourage beneficial species in your garden, you should add variety to it. The wasps come automatically when they find suitable food.
Frequently asked questions
Are there wasps that have blue wings?
One species is often confused with wasps, hornets or bumblebees. The large carpenter bee belongs to the family of true bees, which together with numerous black wasps form the suborder of waist wasps. It is also called the blue-black or violet-winged carpenter bee because of its striking wing color. Carpenter bees need rotten wood to nest and have a high heat requirement. Since suitable habitats are disappearing, the species is listed on the warning list of endangered species in Germany.
Which black wasp builds bag-shaped hanging nests?
Sceliphron species are predominantly native to tropical Africa and are known for their unusual nests. The females collect moist earth and clay to build nests. They use the material to create a fist-sized nest made up of several cells. These hang on plants, rocks or walls and are reminiscent of brown paper bags. It is not uncommon for the nests to be transported to other parts of the world by humans if they are found on the goods. This allowed some species to spread into the Mediterranean region.
Do black wasps form colonies?
Insects that form societies are highly developed. There are some families of waist wasps with this way of life. These include ants, wasps and bees. Colony wasps can be recognized by their striking coloring. All black wasps live solitary lives. They follow predatory or parasitic lifestyles and feed on mosquitoes, aphids, spiders and flies. Other species have specialized on a plant-based diet.
Are there tiny black wasps that look like flies?
Gall wasps are usually one to three millimeters long and rarely eight millimeters long. With this body size, the predominantly black waist wasps can easily be confused with small flies. These legimens place their eggs in plant tissue. The larvae trigger the typical growths in the leaf tissue, which become visible as plant galls. With this way of life, insects represent an exception within the legimen. Gall wasps often live on oaks, maples or rose plants.






