- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
They occur from spring to autumn and leave clear traces of feeding: green caterpillars are not welcome guests in the garden. But a wide variety of species develop from living creatures. They all have a more or less limited range of food.

What types of green caterpillars are there in the garden?
Green caterpillars are larvae of various species of butterflies such as white butterflies, hawk moths, frost moths, noble butterflies and knight butterflies. They appear from spring to autumn and feed on garden plants. The most striking green caterpillar species include the large cabbage white butterfly, the small cabbage white butterfly and the frost moth.
Identify green caterpillars
Nature doesn't make it easy for hobby gardeners when green caterpillars suddenly start eating lettuce. It can be the caterpillars of day and night butterflies as well as the larvae of hymenoptera such as sawflies. Body coloration is variable. There are yellow-green to black-green specimens and some shine a poisonous neon green. Among the butterfly caterpillars there are mini specimens of a few millimeters (like the caterpillar of the Iridescent butterfly) or large larvae that can be up to 8 cm long (like the caterpillar of the evening peacock eye).
Typical identifying characteristics:
- Head: like the body or differently colored
- Hair: densely hairy caterpillars with long or short hair or hairless
- Drawing: with dots or stripes
- Excrescences: spine or hump
- Pairs of legs: Butterflies with five to eight pairs of legs

Whites
Caterpillars from the white family are well camouflaged thanks to their green and brown coloring. Nevertheless, conspicuous markings in warning colors can be seen to protect themselves from predators. Some species feed on poisonous plants and absorb the toxic ingredients, so that the caterpillars are also poisonous to predators. White caterpillars have fully developed pairs of legs on their abdomens. They have short or long hair, although in some species the hair only develops in later caterpillar stages.
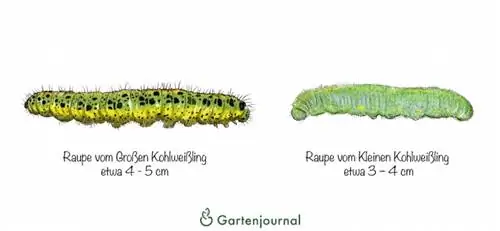
Large and small cabbage white butterfly - caterpillars in comparison
The caterpillars of the large cabbage white butterfly are initially light yellow in color and have a brown head. They molt four times and become progressively darker. Older caterpillars have a yellowish body with black dots that vary in size and are arranged in rows. Their head turns black and the body becomes increasingly hairy, while younger stages appear hairless.
On the other hand, the caterpillars of the Lesser Cabbage White are a dull light green color with yellow stripes on the sides and back, which is typical for the species. Unlike the greater cabbage white butterfly, this species does not undergo any significant changes during its caterpillar development. All stages have white hairs and the coloring remains largely the same.
Swarmers
Caterpillars with a stinger on their backs look threatening. This outgrowth is the so-called anal horn, which is considered a typical identifying feature of hawkmoths. It sits on the eighth segment of the abdomen and in some species can be severely reduced to a button-shaped elevation in the final instar.
| Main coloring of the thorn | different spine coloring | Special feature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linden hawkmoth | with blue spike | purple shimmer | triangular head capsule |
| Morning hawkmoth | with red spike | partly orange nuances | Caterpillars up to 12 cm long |
| Privet Hawkmoth | with black spike | colored light yellow at the base | with purple-white stripes on the sides |
| Pine Hawkmoth | Spine dark and split at the end | later reddish | with orange head |
Background
Swarmers and their anal horn
The anal horn has no specific function. It is intended to protect the caterpillars from predators, because such a stinger has a threatening effect on birds and other insectivores. He pretends that the caterpillar is poisonous. However, the impressive caterpillars pose no danger to people or pets.
The bright colors of the stingers in combination with the dot and line-shaped markings of many caterpillars intensify the threat. Even if the thorn recedes in the later caterpillar stage, the growth still retains its deterrent function. As a button-shaped elevation, the thorn looks like a kind of eye.
Frost tensioner

The movement of the frost moth is worth a photo
The caterpillars of these moths have a peculiar way of locomotion, which is typical of all species in the peeping family. They differ from other butterfly species, which have four pairs of ventral feet, by having one pair of ventral feet. In addition, tensioners have three pairs of sternum bones and the so-called pushers. To move around, they cling to a branch with their breastbones and pull their abdomen up to their chest. This causes the body to arch upwards in an omega shape. The caterpillar pushes itself forward with the help of its pushers and the pair of abdominal feet.
Typical coloring of the caterpillars:
- adapted to environment
- some species imitate small branches
- Small frost moth: light green with white stripes on the sides and dark lines on the back
- Large frost moth: red-brown with light spots
Food Spectrum
The caterpillars of the large and small frost moth feed on young shoots, leaves and flower buds in spring. They attack fruit trees and do not stop at wild or ornamental shrubs. In the event of a severe infestation, the tree is damaged, leaving only the leaf veins and droppings on the tree. As soon as the food is used up, the larvae look for other sources of food. Therefore, in spring, green caterpillars can be observed on threads, which are carried by the wind to other trees.
Edelf alter
Among the noble butterflies there are caterpillars with hair or thorns that look threatening and fascinating at the same time. The thorns are simple or branched. Their body markings are very variable. The caterpillars can have black stripes or light and dark lines in different colors. Some species live socially on their food plants.
This is what typical caterpillars look like:
- Little fox: black with two broken yellow lateral lines, yellow and black spines
- Monarch butterfly: band pattern of white, black and yellow horizontal stripes
- Painted Lady: light yellow to green-brown, dark pattern
- Forest board game: yellowish-green, dark green and white edged dorsal stripe, light and dark lines on the sides
Rittermoth

The caterpillars of the knight butterfly are green or yellowish in color
Typical of the caterpillars of knight butterflies is the brightly colored neck fork that sits between the head and body. In case of danger, this can be pulled out so that predators are deterred. To do this, the head and the front segments of the body are pulled downwards. The neck fork gives off an unpleasant smell.
Swallowtails belong to the family of knight butterflies. Their caterpillars are initially black in color and have orange-red dots. The white saddle spot, which is said to be reminiscent of bird droppings, is typical. Older caterpillars are green in color and have black horizontal stripes with orange-red or yellow dots. They occasionally appear in gardens when dill, carrots or fennel are grown there.
Caterpillars of other insects
Some larvae of other insects can easily be confused with butterfly caterpillars. There are green-colored sawfly caterpillars with a black head or yellow, brown and black stripes and with brown to black dots. However, most of these caterpillars are not harmful to plants. They can be identified by their pairs of legs. In addition to the three pairs of sternums, these larvae develop up to four additional pairs of ventral feet and a pair of legs at the end of the body called pushers.
Green caterpillars are not always the larvae of butterflies.
When can green caterpillars appear?
In which months the caterpillars are active depends largely on the weather conditions. When temperatures are mild, the period of activity can extend. In some cases, the caterpillars of various species of butterflies can be observed all year round. Many lettuce eaters can be observed to a lesser extent. Their occurrence is concentrated in the summer months, because that is when most forage plants grow.
| Main month | Coloring | Distinguishing features | Food | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agate Owl | March - October (-December) | green to yellow-brown | Back with white line, interrupted | Nettle, blackberry, culinary herbs, salad |
| Gamma Owl | March - October (-December) | green, yellowish or bluish | Black markings on the head | Nettle, dandelion, culinary herbs, salad |
| Small frost moth | April - June | green | white longitudinal lines | Deciduous trees |
| Pyramid Owl | May - June | teal | Humps on the abdomen | Oak, poplar, willow |
| Small Cabbage White Butterfly | August - October | light to dull green | yellow side and back stripes, white pigments | Cabbages and vegetables, nasturtiums, rapeseed |
Fighting green caterpillars?

The boxwood borer can become a pest and eat entire trees bare
Whether control measures are necessary can only be determined after the species has been precisely identified. Very few species are harmful to the plants in the garden and therefore do not need to be controlled. The caterpillars of the large and small frost moth or the box tree moth are able to eat entire stands of plants. If the infestation is small, you can simply collect the caterpillars. Check your ornamental plants regularly to take further control measures if necessary.
Ornamental plants
The green caterpillars of the boxwood moth are spotted with black. They eat the leaves and bark of the boxwood until it is completely bare. Since the ornamental plant can be damaged, the caterpillars should be combated early.
The light to dark green caterpillars of the hedge moth with a brown head feed on roses like the caterpillars of the frost moth. Caterpillars with orange heads come from sawflies.
If your lilac is infested with green caterpillars, it may be the privet moth. The densely hairy caterpillars of the Pelargonium Blueling settle on geraniums. These are colored yellow to green and have one to two pink longitudinal lines on their backs.
Vegetables and fruits
Various butterfly caterpillars occur on kohlrabi, cauliflower or broccoli. In addition to the caterpillars of the common cabbage white butterflies, green, brown or dark brown caterpillars of cabbage and vegetable owls can also feed on the plants. Much more inconspicuous is the greenish to yellow larvae of the cabbage moth, which targets heads of cabbage. Covering the plants with cultural protection nets (€33.00 on Amazon) helps against pests so that the adult butterflies are prevented from laying eggs.
More caterpillars in the kitchen garden:
- Strawberries: agate owl, borer or sawfly larvae
- Peppers: Owl butterflies like the vegetable owl
- Salad: Gamma Owl, Frost Moth
Tip
To detect an infestation early, you should check the soil for droppings and eaten leaves. The caterpillars usually don't show themselves at first glance.
Trees and bushes
Green caterpillars are often active on fruit trees such as apple trees and cherry trees in summer, which later develop into frost moths. These moths also attack shrubs such as currants and gooseberries. However, these fruit trees can also be visited by gooseberry sawfly caterpillars. Regardless of whether it is a frost moth or a sawfly - the caterpillars can eat the trees completely bare and should be destroyed early.
It's completely different with the birch moth. The species is increasingly disappearing as its natural habitats are being lost. Therefore, she is now on the warning list. The pale green caterpillars have fine black spots and feed on the leaves of various birch plants. They occur not only on birch trees but also on black alder, hazel and winter lime.
kitchen herbs

The owlet caterpillar likes to eat our vegetables
Owl butterflies have a wide range of food. The species attack almost all herbaceous plants. Gamma-ray and agate owl are two of these species that can also occur on basil, mint and parsley. The well-camouflaged caterpillars are usually difficult to detect. A good indication of a caterpillar infestation are small balls of feces on the ground.
Tip
Since you still want to eat the culinary herbs, you should not use soft soap, tobacco, etc. Instead, stick a clove of garlic into the soil.
Frequently asked questions
Are green caterpillars with stingers on their backs poisonous?
The spines that pine, linden or privet moths develop on their abdomens are the so-called anal horn. This serves to deter predators. In the course of development, in some species the outgrowth can recede, leaving an eye-shaped bump behind. This thorn poses no danger to humans.
How can I fight green caterpillars naturally?
Protective nets are the simplest solution to prevent caterpillar infestation. These prevent the butterflies from laying eggs. If your plants are lightly infested, you can simply collect the caterpillars. Release the trapped animals in the forest so that they can look for alternative food plants.
If there is a more severe infestation, you can spray robust plants and bushes with a jet of water. Then collect fallen larvae from the ground. Caterpillars are guided by scents. Strong-smelling plants such as garlic confuse the insect larvae. Mixed cultures therefore prevent caterpillar infestation.
How do I recognize an infestation by green caterpillars early?
No matter whether they are small, fat, large or long caterpillars - they all leave traces of feeding on the leaves. Inspect your plants thoroughly and don't forget to check the undersides of leaves and branches. Many caterpillars are adapted to their environment and are therefore usually not visible at first glance. Fecal crumbs are a good guide. They can be seen as dark spots on the plant.
When and where do green caterpillars appear?
The voracious larvae can appear in the garden from March to October, although their activity period depends on the weather. During cold and rainy spring periods, the butterflies do not lay their eggs on the food plants until summer. If winter is delayed, offspring can be produced until December. Almost all plants are attacked by caterpillars in nature. Many species have specialized, while other butterfly caterpillars occur on various ornamental and crop plants.






