- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:22.
Behind the vegetable owl is not only a popular recipe for children's birthday parties, but also a harmful insect. Butterflies and caterpillars lead a hidden life, while their tracks are clear. With the right measures you can combat the pests.

How do you fight the vegetable owl in the garden?
The vegetable owl is a pest whose caterpillars prefer to eat vegetables such as tomatoes, lettuce and cabbage. To combat it, natural enemies such as predatory bugs can be used, or biological agents such as Bacillus thuringiensis and neem oil can be used. Protective nets and mixed cultures help preventively.
Identifying vegetable owls
Children love the vegetable owl, while hobby gardeners tend to fear it. The vegetable owl is an insect whose caterpillars prefer to attack tomatoes in the greenhouse. It is not uncommon for leaves to be pitted and fruits to show traces and remains. If there is superficial damage, you can still process peppers and tomatoes. Thoroughly wash off traces of feces and remove any damaged areas. In the vegetable owl, damaged vegetables are no longer noticeable and the children enjoy the colorful creation with dip best.
| Prime flight time | Special features | |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetable Owl | May to June | ring and kidney-shaped spots |
| Changing Herb Owl | April to June, July to September | Distinct wavy line, extends into the wing fringes |
| Pea Owl | May to August | indistinct W-marking, noticeable v-spot |
Features

The vegetable owl is an inconspicuous moth
Vegetable owls are among the moths that are widespread in Europe and can be observed twice a year under optimal weather conditions. They first appear between mid-May and the end of July. The next generation flies from early August to mid-September. Their wingspan is about four centimeters. The forewings of adult butterflies are colored brown-red, while the hindwings have a light reddish basic color. There are different color variations. Occasionally specimens with yellow-red or black-brown forewings can be observed.
Patterns and drawings:
- indistinct transverse lines, some of which are missing
- gray and reddish lines, ring or kidney-shaped
- white W drawing
Development
Females lay their green colored eggs on suitable food plants. The caterpillars hatch after about a week. The caterpillars shed their skin five to six times between September and October. After 30 to 40 days, pupation occurs underground in a dark reddish-brown cocoon in which the caterpillars overwinter. These caterpillars represent the first generation. Second generation caterpillars develop between August and September.
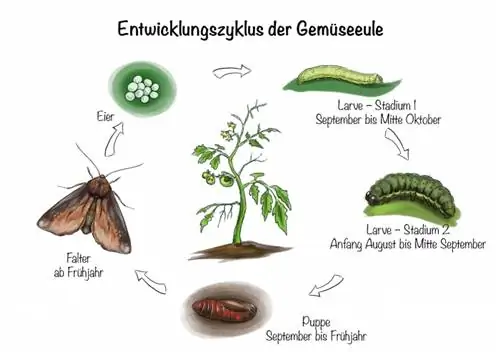
Caterpillars
Like the adult butterflies, the voracious offspring are nocturnal and hide during the day at the base of their food plants. This makes the plant pests difficult to detect. Occasionally the caterpillars can be observed in an elongated position on the leaves during the day.
Detecting caterpillars:
- Length up to 45 millimeters
- variable body coloring: green, brown, gray or pink
- fine white spots
- wide, pale yellow to white line
- yellowish to greenish brown head
Food plants of the vegetable owl
The butterfly likes to come into the light and can be observed on various flowers. The preferred nectar donors include Canadian goldenrod, morning glories, common waterbush or butterfly lilac. The caterpillars feed on plant tissue. They do not specialize in any type of food and eat both leaves and fruits. They often appear on tomatoes, peppers and lettuce.
Food plants for the caterpillars:
- Vegetables: cabbage, peas
- Fruit bushes: currant, blackthorn
- Ornamental plants: cyclamen, common heather, small toadflax
- Weeds: dock, nettle

Fighting vegetable owl
The caterpillars of the vegetable owl cause great damage to both commercial vegetable cultivation and private gardens. The species is of little importance as a field pest because of the use of insecticides. When growing your own vegetables, you should avoid using chemicals and combat pests organically.
Nematode caterpillar control
Nematodes are suitable for controlling pests that prefer to live in the soil and feed on plant roots. That is why they do not have their full effect on the caterpillars of the vegetable owl. They can still be used to reduce stock density. If the caterpillars attack root vegetables such as carrots, nematodes of the type Steinernema carpocapsae can be a useful measure.
Destroy butterflies with pheromone trap
The traps attract male moths with species-specific sex hormones. When you try to land, these stick to the glued surface and can no longer escape. Although this measure prevents the males from mating, a severe infestation by the vegetable owl cannot be eliminated with any pheromone trap. Such products are suitable for control purposes, although they should only be used in the greenhouse.
Natural enemies

Predator bugs eat herbivorous pests
Predator bugs are active hunters that lurk on flowers or crawl through the vegetation and seize various prey. Live insects can be purchased from specialist retailers. Place predatory bugs and larvae at different points in the greenhouse so that the beneficial insects can start hunting immediately. Storage is possible but should be avoided. The longer you wait before spreading, the more predatory bugs can die due to lack of food.
Store correctly:
- no longer than one or two days
- at temperatures between eight and ten degrees Celsius
- in the dark
Excursus
How predatory bugs hunt
The insects do not specialize in any particular prey. They hunt arthropods and insects that can be much larger than themselves. Robber bugs and their nymphs hold prey with their strong and sometimes hairy legs. They insert their long trunks into prey to inject saliva. This paralyzes the prey and causes the internal organs to decompose. The predatory bugs just have to suck out the juice.
Neem oil
The oil of the neem tree contains azadirachtin, which has an insecticidal effect. It is often advised that a few drops of neem oil can be added to the irrigation water. The plants should absorb the ingredients and transport them into the leaves. These taste bitter, so the caterpillars look for other food plants. Nothing is known about the effect of this method.
Neem oil is, however, successfully used as a contact insecticide. If you spray the affected plants with a low-dose solution of water and oil, it will have a fatal effect. Please note, however, that products containing neem oil extract are legally recognized as an insecticide and certain regulations apply to their use in private gardens. The ingredient does not have a selective effect and also harms beneficial insects.
Products containing neem oil extracts are legally considered insecticides and should be used correctly.
Bacillus thuringiensis
The bacterium occurs naturally in the soil and often lives in association with plant roots. It produces certain toxic substances that are fatal to some insects. These toxins are used to combat harmful beetles, cutaneous insects, dipterans and butterflies. The substances have no effect on plants and vertebrates.
This is how the bacteria works:
- secrete proteins that attach to intestinal cells
- these create pores in the cell wall
- Intestinal cell is destroyed and organism dies
Tip
There are different products for spraying. Please note the information in the package insert, as such products are only approved for certain areas of application and plants.
Prevention
To prevent pests from spreading, you should protect your plants from the voracious caterpillars. In general, mixed cultures help to keep pests in check naturally. There are enough beneficial insects here and many plants give off repellent smells.
Borago officinalis

The smell of the beautiful Borago officinalis is said to deter vegetable owls
Borage is a plant from the roughleaf family that is used in the kitchen as a spice or vegetable. Its blue flowers are rich in nectar and attract honey bees. The scent is said to have a deterrent effect on vegetable owls, preventing female butterflies from laying eggs. Put some plants between your tomatoes and watch how the butterflies behave.
Protective nets
So that the butterflies are efficiently prevented from laying eggs, you should stretch protective nets over your vegetable plants. Check your plants regularly for pest infestation. Caterpillars can be collected by hand and placed on another food plant in nature.
Tip
Chickens are efficient pest controllers. They scratch in the ground and pick up the resting caterpillars.
Frequently asked questions
How common are vegetable owls?
The natural habitats of the vegetable owl include river floodplains, swamp forests and valley floors. However, it is a cultural successor and widespread in Europe. The butterflies mainly inhabit cultivated landscapes such as parks, gardens or wastelands with suitable food plants. They do not specialize in any particular plants, but feed on species from different genera. The caterpillars can often be observed on tomatoes and peppers.
How do I recognize an infestation by the vegetable owl?
The caterpillars feed on the soft leaf tissue. They leave traces of feeding on the leaves and occasionally attack fruits or roots of vegetable plants. During the day, the caterpillars hide at the base of the stem or stretch out in the sun on a leaf. Because of their green color they are difficult to recognize. They curl up when touched.
What can I do against an infestation by vegetable owls?
Protect your plants with close-meshed nets so that the female butterflies can no longer lay their eggs. If you find caterpillars, you should collect them and place them on an alternative food plant such as nettle. Products containing neem extracts should be used carefully as they are not selective. Supportive measures for combating include predatory bugs and nematodes or special bacteria.
How to make an owl out of vegetables?
Tomatoes form the owl's body, which is filled with cucumber slices. Use pepper strips as wings and beak. Mix cream cheese with garlic and mint and pour the dip into two equal-sized containers. With an olive in the middle, the bowls act as eyes






