- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-25 17:45.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:22.
Apricot trees can definitely be propagated at home. But the usual and well-known methods in home gardens, such as sowing and propagating cuttings, are not the first choice here. Apricot trees are mainly grafted. This is how it works in detail.

How do you graft an apricot tree?
Apricot trees are propagated through grafting by transferring a noble bud from a desired donor tree to a suitable rootstock, usually plum or cherry plum. The refinement takes place from July to September, where the precious bud is carefully inserted into a previously prepared interface and fixed.
What is refining anyway?
When grafting, a part of another tree is “transplanted” into a tree. A scion or a noble bud is used for this. While the first tree from now on only serves as a base, the crown develops according to the new genetic material. This is intended to ensure that the tree bears different or desired fruits.
Advantages of finishing
This method creates an identical copy of the apricot tree that provides the finishing material. If the tree were to be propagated from seeds, the result would always differ from the mother tree. But in this way desired properties can be safely retained.
The base can also be selected according to properties that are useful. Their root system is usually more resilient and suits the soil conditions better than that of the noble variety.
Suitable underlay
To refine an apricot, you need a tree that is suitable as a base. This fruit tree harmonizes with any variety except cherries. However, it is usually refined to a plum or cherry plum.
Optimal timing
The best time for inoculation, as the finishing process is technically called, depends on the base used.
- on plum: July to early August
- on apricot and peach: in August
- on almond: August to mid-September
Note:Travel refinements can also be done in spring. However, this is more demanding because the scion can dry out quickly.
Edelbud
This is cut from an already grafted apricot tree, whose fruit characteristics should be taken over by the newly grafted tree. It must be carefully separated from the shoot, leaving a piece of the shoot or bark attached.
Tip
It is possible to refine several types of fruit on a single surface. This makes it possible to cultivate different varieties in a space-saving manner.
Refining office
The base can be refined in various places. Above the spot, the tree will develop according to the genetic material of the noble bud. A distinction is made between:
- Root neck grafting
- Crown or head refinement
- Framework finishing (within the crown)
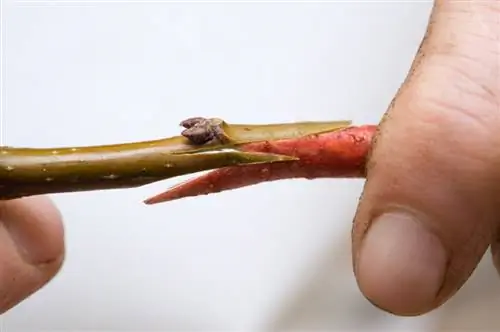
Refining process
The bark of the base is scratched at the selected finishing point. The two cuts are arranged so that together they form the letter T. A special eyelet knife (€12.00 on Amazon) is helpful here.
- Score 3 cm vertically, 2 cm horizontally
- remove both bark wings from the trunk
- Remove the precious eye from the wooden sign
- Fit the eye firmly into the prepared opening
- Cut off any excess pieces
- Place the bark flap over it again
- Connect oculation site
It takes about six weeks for the planted material to grow. If it loses its green color in the meantime, the refinement has failed. If the eye continues to pop out, you'll know the effort was worth it.