- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-25 17:45.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:22.
Depending on how the lawn is used, the fertilization times and the frequency of fertilizer application differ. Fertilizing a rarely used lawn in October is good for maintenance purposes. The lawn with normal use enjoys three to four applications of fertilizer from spring to autumn. If you apply too much fertilizer - especially when using artificial fertilizers - the lawn can show signs of burns.

How is lawn fertilized?
Due to weather conditions, the load on the respective area and general consumption, the nutrients present in the soil steadily decrease over time. The mineral depots must therefore be replenished once or several times a year. This promotes the he althy growth of the lawn and the absence of unwanted weeds and moss.
Does lawn need to be fertilized?
Yes, because mowing the lawn requires a continuous and sufficient supply of nutrients. In addition, the nutrient concentration in the soil substrate is constantly decreasing due to leaching and consumption. In classic lawns, the depots can only be filled up by applying external fertilizer.
Nevertheless, you shouldnot constantly fertilize. A constant supply of nutrients can lead to over-fertilization. This manifests itself in yellowing of the stalks. The cause is the impaired water absorption of the roots due to the prevailing imbalance. Therefore, follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the frequency of fertilizer application to ensure an optimal ratio.

Fertilizing your lawn at the wrong time can cause irreparable damage. Not only the time but also the distance from the last fertilization plays a crucial role.
Nutrients that lawns need
Anyone who deals with the topic of fertilization will sooner or later come across the term NPK fertilizer. This cryptic abbreviation stands for the chemical names of the minerals it contains: nitrogen (N), phosphate (P) and potassium (K). For he althy and strong growth, the lawn primarily needsNitrogen,Phosphate,Potassium,MagnesiumandIron
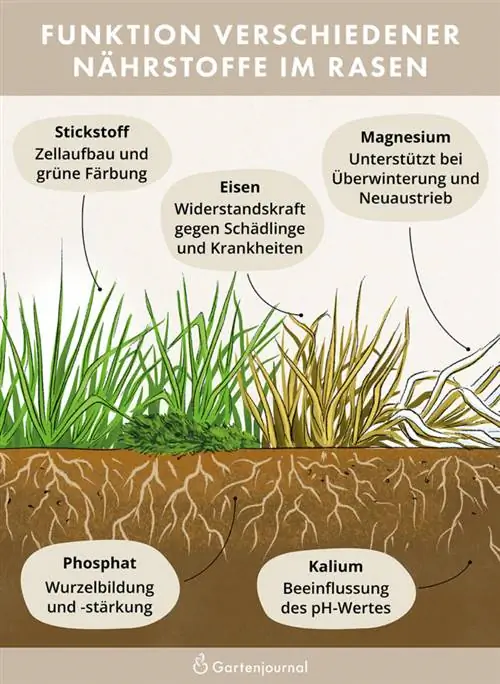
Nitrogen: In addition to general growth, the mineral is required for chlorophyll formation and cell structure. Nitrogen is therefore essential for the lush green color of your lawn. While nitrogen deficiency leads to increased weed growth, over-fertilization causes uneven growth, combined with stunted growth. Applying the optimal amount is therefore crucial.
Phosphate: Phosphate is the essential engine for root formation and strengthening. The nutrient is irreplaceable for a stable stalk base.
Potassium: Potassium is primarily responsible for influencing the pH value. For optimal nutrient and water absorption, a value between 5.5 and 6.5 is recommended. Potassium acts as an acid and lowers pH. Over-fertilization can therefore permanently destroy the delicate balance of the soil, which is why caution is required when applying it.
Magnesium and iron: Magnesium and iron round off the nutrient package for a he althy lawn. The former helps the plant overwinter and produce new growth in spring. Iron, in turn, increases resistance to diseases and pests.
Organic and mineral lawn fertilizers
The range of commercially available fertilizers is very diverse. The most important distinguishing criterion is origin. While organic fertilizers consist of natural components, mineral products are characterized by industrial production.
| Fertilizers | Composition | Advantages | Disadvantages | Shape | Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | S alts | direct provision of nutrients, suitable for acute nutrient deficiency | Leaching in high humidity, risk of over-fertilization, resource-intensive production | Granules, liquid | Blue grain, lime ammonium nitrate, mineral liquid fertilizers | |
| Organic | vegetable or animal remains | long-term improvement in soil quality, no risk of over-fertilization, nutrition of the microorganisms present in the soil | Longer duration of effect due to slow decomposition, individual varieties do not contain all the necessary nutrients | solid, liquid | Manure, manure, (compost), horn shavings, manure |
Depending on the condition of the lawn, one or the other variant may be more suitable. Especially in the case of acute deficiency symptoms, the administration of mineral fertilizers is significantly more effective due to their quick effect. Organic fertilizers are more suitable for fertilizing fundamentally he althy areas due to their longer duration of action. In addition, harmful over-fertilization is impossible with the natural variants.
In practice, liquid fertilizers based on minerals and blue grain are particularly popular. Both species are characterized by a high concentration of the most important nutrients. They are therefore also referred to as complete fertilizers.
With reference to the properties of mineral fertilizers already presented, they should be used sparingly and generally only if defects exist. If added excessively, there is a risk of over-fertilization. This can result in the turf dying and increased environmental pollution. The use of industrial products can also have an impact on soil quality and groundwater. Therefore, use this type of fertilization only with caution and in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Alternative fertilizers
There are many alternatives to commercial fertilizers. Home remedies and waste are particularly common. These are often free and easy to obtain. Coffee grounds, compost and horn shavings are known from fertilizing perennials and vegetables.
Coffee grounds: Used coffee grounds are a common waste product. However, it still contains large amounts of potassium, nitrogen, phosphate and other antioxidants. It is therefore also suitable as a fertilizer for your lawn. Due to the positive effect on the grass, moss in particular is effectively combated. An application of around 50 grams per square meter twice a year is sufficient.
Compost: Almost all cutting waste can be used. With the addition of compost additives, a homogeneous mass is created over time, which can be distributed with a rake. Compost is rather unsuitable as a fertilizer for the lawn because of its soil-covering effect. This cuts off the turf from the air, which in the worst case scenario can lead to the entire area dying.
Horn meal and horn shavings: Horn shavings are produced industrially from hoofs. Compared to horn meal, the individual pieces are up to one centimeter in size. Horn flour, on the other hand, has a very fine consistency. Due to the high nitrogen content, both products are in principle very suitable for fertilizing plants. However, horn meal should be preferred for fertilizing lawns due to its consistency. In most cases, the coarsely chopped pieces of horn shavings do not end up directly on the ground, but remain attached to the stalks. The flour, on the other hand, falls past the stalks due to its fine shape.
Excursus
Micro clover and BOKU lawn
Micro clover and BOKU lawns are recognized alternatives to conventional meadows. In addition to its very dense growth, microclover impresses with its ability to store nitrogen from the air in its roots and continuously release it into the environment. Thiseliminates the need for annual fertilization of the areas, the lawn takes care of itself.
BOKU lawn not only consists of grasses, but also contains herbs and flowers. Compared to conventional lawns, these mixtures are often not as resilient, but are significantly more valuable from an ecological perspective. Sowing with BOKU lawn is particularly useful for areas that are rarely used. Due to the low growth height, cutting once or twice per year is sufficient.
Use of lawn lime
Lawn lime is generally recommended as a proven fertilizer for the lawn. However, it should be noted that lime does not contain any nutrients. So it isnot a fertilizer in the true sense.
Nevertheless, adding lime is a useful addition to normal fertilization, especially if the pH of the soil is outside the normal range. A pH value that is too low means acidic soil. This often contains very few microorganisms and the absorption of nutrients is hardly possible. By applying lime, the substrate becomes more alkaline, i.e. the pH value increases.

Applying lawn lime is a proven way to adjust the pH value of the soil. But the same applies here: Over-fertilization with lime can have massive consequences for the lawn.
The simultaneous application of lime and fertilizer should be avoided. The ingredients create undesirable reaction products that can damage the lawn. Therefore, lime at least four, preferably eight weeks before the planned fertilization. It is advisable to fertilize in spring and lime in autumn.
Before you treat your lawn with lime, you should definitely determine the current pH value of the soil. A pH value that is too high also makes mineral absorption more difficult, but is much less favorable than a pH value that is too low. With the Neudorff soil test (€4.00 at Amazon) you can use a color scale to determine the current pH value and determine the amount of lime required. Even without prior knowledge of chemistry, soil analysis can be carried out easily in just a few minutes.
When to fertilize
For a commercial lawn,one to four fertilizations per year are possibleFertilization is possible from spring through early summer and summer into autumn. The earliest and latest timing essentially depends on the temperature conditions. Ideally, fertilization should take place outside of the frost-free period. As a rule, fertilizationis possible from March at the earliest and until Octoberat the latest. At least during the day temperatures should still be around 15 degrees Celsius.
Fertilization in spring (promote sprouting):
Fertilization in spring primarily serves to activate the lawn after winter. Therefore, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are particularly recommended at this time. To support the first growth spurt, we recommend fertilizingbetween March and May Scarifying the lawn in spring is recommended as additional lawn care. In this case, however, you should wait until April. The subsequent spring fertilization should then only be carried out two weeks apart. This gives the lawn a break and reduces stress.
Fertilization in early summer (preparation for summer):In addition, you can fertilize again in early summer with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer. Between the end of May and the end of June you can optimally prepare your lawn for the coming summer. Potassium also strengthens resistance to drought stress and prevents the lawn from dying even in prolonged drought.
Fertilization in autumn (preparation for winter):The last fertilization in autumn is primarily used to prepare for the coming sub-zero temperatures. The additional administration of potassium, magnesium and phosphate strengthens the roots and resistance to cold. For an optimal mix, we recommend using a special autumn lawn fertilizer. However, to ensure optimal release, the fertilizer should not be applied too late. Organic fertilizers are therefore less recommended for autumn fertilization. However, if you decide to fertilize organically, you should apply it early in late August or early September. Fast-acting mineral fertilizers, on the other hand, can be applied until October.
Frequency of fertilization
The frequency of fertilizationdepends on the demand on the lawn While heavily used areas should be supplied with new nutrients up to four times a year, less used areas only need an annual refreshment. However, in order to avoid over-fertilization, it is important to ensure sufficient intervals, especially when fertilizing several times a year.
One-time fertilization:
One-time annual fertilization is only recommended onlittle-used areas. It serves to maintain and continually replenish nutrient depots. The one-off fertilization usually takes place in autumn to optimally prepare the lawn for winter. The ideal time to apply autumn lawn fertilizer is betweenSeptember and October The nitrogen contained in the long-term fertilizer also ensures a sufficient supply of this mineral.
Two-time fertilization:
Two-time fertilization is applied tomoderately used areas. The fertilization intervals are significantly longer here, but this is completely sufficient due to the lower use. Starting fertilization with a nitrogen-containing fertilizer for activation usually takes place inAprilIn this case, additional fertilization in the summer for preservation is not necessary. Autumn fertilization in conjunction with preparing the area for colder temperatures takes place inAugust/September
The summer months in particular are very stressful for grassland due to heat and drought. Autumn fertilization is therefore very important. In addition, the lawn only has sufficient winter hardiness with the right combination of active ingredients. The Plantura organic autumn lawn fertilizer is characterized by an optimal combination of active ingredients of potassium and nitrogen, which contributes to high frost hardiness. In addition, the natural ingredients stimulate the microorganisms in the soil. The granular form enables easy and low-dust distribution of the fertilizer.
Three to four times fertilization:
Three to four times fertilization of lawns is only recommended forheavily used areasrecommended. The high stress results in a higher nutrient requirement, which can only be met through a continuous supply of suitable fertilizer. In practice, fertilizer applications in spring, early summer, summer and autumn have proven to be effective. The interval between individual doses should ideally be at least eight weeks. This avoids over-fertilization due to excessive mineral concentrations, which in turn can lead to damage to the lawn. For even application, we recommend the monthsMarch,June,August(only with four fertilization applications) andOctober
For spring and summer fertilization, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are primarily recommended. These fertilizers act as growth promoters, especially after winter. The Plantura organic lawn fertilizer impresses with its 100% organic ingredients combined with a sustainable, long-term effect. The combination of corn gluten, wheat gluten, nut shells and potassium sulfate creates an effective mixture that optimally meets the needs of the lawn. The granules are very economical, so that an amount of 10.5 kilograms is sufficient for an area of 250 square meters.
Apply lawn fertilizer
Lawn fertilizers are usually used in solid form as granules. This results in various application options, such as using a spreader. This enables even distribution by setting a fixed spreading strength. Dispensing by hand is much more difficult to coordinate. Although no additional tools are required here, uniform application is only possible with practice. This variant is only recommended for professionals, especially to avoid overdosing or underdosing. You can find clear purchasing advice for suitable gritters here.
Regardless of the method of application, distribution in both the longitudinal and transverse directions has proven successful. Bymoving crosswise the lawn area achieves the best possible distribution.

Using a lawn sprinkler or sprinkler ensures even moistening of the lawn. This allows the fertilizer to dissolve and release its ingredients.
After fertilization, shallowirrigation is absolutely necessary. This loosens up the dry fertilizer and gradually works it into the soil. Even moistening is achieved with a sprinkler. You can find some helpful tips on using automatic watering here. Alternatively, if rain is forecast, this is also suitable. In any case, pay attention to the weather forecast. Too much water can cause the fertilizer to be washed away and not be able to develop its effect.
FAQ
How is lawn fertilized?
Lawn is best cared for with a special lawn fertilizer. While products containing nitrogen are preferred in spring and summer, the lawn needs a mixture containing potassium in autumn. For even distribution, we recommend using a spreader whose spreading strength can be individually adjusted. Experienced gardeners can also apply the fertilizer by hand.
When is lawn fertilized?
It is recommended to fertilize up to four times a year: in spring, early summer, summer and autumn. In practice this means fertilization periods from March to May, June to July, August and September to October.
How often is lawn fertilized?
Depending on the demand, up to four fertilizations per year are possible. Lawns that are heavily used should therefore be fertilized four times a year. Less used areas only require one fertilization per year to maintain them.
Can lawns be overfertilized?
Individual fertilizations that are too close together or too high can lead to over-fertilization. This manifests itself in the lawn drying out despite an adequate supply of water. The cause is the resulting imbalance in the soil substrate, which impairs moisture absorption by the roots.
What happens if the lawn is not fertilized?
Due to the decreasing nutrient content in the soil, more and more weak-consuming plants are establishing themselves. These include the well-known weeds that are increasingly pushing back the lawn.






