- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:02.
Roses are one of the undisputed favorites in the garden. However, in order for your rose bushes to grow he althily and bloom profusely, they need the right cocktail of nutrients. In this article we will explain to you which rose fertilizers are suitable and when you should apply them.

Which fertilizer is best for roses?
Suitable rose fertilizers are organic fertilizers such as manure, compost or horn shavings, which provide all the necessary nutrients. Home remedies such as coffee grounds, banana peels and wood ash can also be used. Mineral fertilizers should only be used in combination with organic ones in order not to worsen the quality of the soil.
- Roses have high nutritional requirements and need a balanced mix of different components.
- Basically, two fertilizations per year are planned, sometimes a third for the purpose of potassium supply.
- Prefer organic rose fertilizers as they provide all the necessary nutrients.
- Stable manure, compost and additional home remedies such as coffee grounds, banana peels and wood ash are particularly suitable.
Fertilize roses properly - roses need these nutrients
Roses only show their lavish blooms when they are supplied with an optimally formulated fertilizer at the right time. Not every fertilizer is suitable for supplying demanding trees, because
- theflower formation the “Queen of Flowers” needs lots of nutrients to stimulate bud formation. In particular, the remontant and more frequently flowering varieties have a high nutrient requirement.
- thepromotion of frost hardiness a supply of a balanced nutrient cocktail is essential. The correct composition of the fertilizer and the correct timing of fertilization promotes shoot termination and ensures that new shoots mature in a timely manner before winter.
- thestorage of reserves before winter, the right time is crucial. Roses develop new shoots from these reserves the following year.
- theimproving soil quality a good, balanced rose fertilizer is also essential. Roses need loose, humus-rich soil, which is why the fertilizer ideally stimulates soil life and thus humus formation.
Ingredients and optimal composition
In this article you will find out what is important when caring for roses in spring.

However, to support the rose in its growth and flower formation, it is not enough to simply give any fertilizer. Instead, it's all about the right nutrient mixture at the right time - then rose care will work. You should pay particular attention to these nutrients:
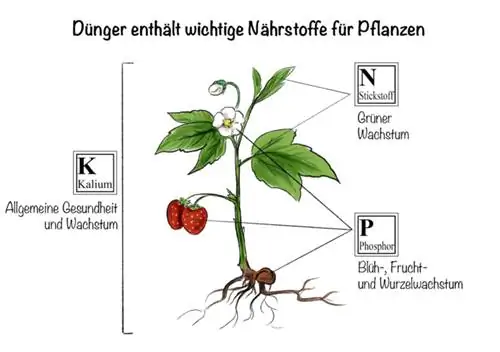
- Nitrogen: important for leaf emergence and shoot growth, therefore administered more in spring, but only weakly in summer
- Phosphor: important for flower formation, apply in spring, for more frequently flowering and remontant varieties also in a quick-acting form in summer
- Potassium: promotes the formation of firm shoots and thus winter hardiness, is mainly administered in summer and autumn
Commercial rose fertilizers contain the above-mentioned and other nutrients, minerals and trace elements in an optimal composition. However, before you use these fertilizers, a soil analysis makes sense. You can have this carried out by an appropriate institute and it will give you information about which nutrients are missing in your soil - and which are plentiful. Many garden soils today are rich in phosphorus, which is why an oversupply should be avoided.
Excursus
When is the right time to fertilize?
Basically fertilize your roses twice a year. The first dose is due at the time of budding in spring, around the beginning of April. The second fertilization takes place after flowering between the end of June and the beginning of July. This fertilizer must work quickly. Make sure that newly planted roses - and ideally plenty of ripe compost - do not need any further fertilization in the year they are planted. You only fertilize these in the second year.
Which rose fertilizers are suitable?
Basically, a distinction is made between mineral and organic forms of fertilizer. Some rose fertilizers also contain a mixture of mineral and organic components, including many organic rose fertilizers. We explain which fertilizer is suitable and when - or not - in this section.
Mineral rose fertilizers

There is a risk of over-fertilization with mineral fertilizers
With mineral fertilizers, the nutrients are in the form of s alts. These rose fertilizers are available to the plants very quickly, but there is also a risk of over-fertilization. In addition, pure fertilization with mineral fertilizers poses the problem that the nitrogen obtained from s alts in particular promotes the breakdown of humus and thus leads to a deterioration in soil quality in the long term. For this reason, you should never rely on pure mineral fertilizers, but instead give preference to a mix of organic and mineral components or purely organic fertilization (plus the addition of primary rock powder). Commercially available complete rose fertilizers generally meet these requirements.
Excursus
Can you fertilize roses with blue seed?
Blaukorn is a so-called NPK fertilizer that is available in purely mineral form. In principle, you can fertilize your roses with it, but we advise against it. Blaukorn has a high nitrogen content, which allows the shoots to grow strongly and neglects the formation of flowers. The roses become bushy, but only bloom a little. In addition, the shoots remain soft, do not harden properly and are therefore more susceptible to pest infestation or rose diseases.
Natural rose fertilizer
Instead of buying rose fertilizer, you can use organic materials from your own garden - or from your neighbor - instead. The raw materials presented here are particularly suitable for roses. Purely organic fertilization offers several advantages:
- The roses are continuously supplied with nutrients over a longer period of time.
- Over-fertilization is practically impossible.
- Organic fertilization promotes soil life and thus humus formation.
- You can gradually improve the soil with organic fertilization.
In addition, manure, compost, etc. ensure that the natural nutrient cycle is maintained.
stable manure
Due to the balanced nutrient composition, cattle dung or horse manure (with straw!) are particularly suitable for fertilizing roses. However, you should not use fresh manure as it is too harsh and could damage the plant. Instead, let the manure mature well (e.g. on the manure heap or with the compost (€15.00 on Amazon)) or use commercially available pellets. These are made from dried manure and also have the advantage of not smelling.
Compost
Humus is an important soil component for roses, which is why you can fertilize them very well with mature garden compost. When planting, put a shovel per rose into the planting hole to create optimal starting conditions. When fertilizing in spring, the compost can be supplemented with a handful of horn meal or horn shavings to supply the nitrogen that is important for growth. Primary rock flour, in turn, ensures a balanced mix of minerals and trace elements.
Horn shavings / horn meal
Horn shavings, horn meal or bone meal is rich in nitrogen. Add this organic fertilizer to the mandatory compost or manure application in the spring. However, the material is not suitable as a sole fertilizer due to the lack of balance.
Suitable home remedies

Wood ash is a great fertilizer for roses
“When a flower blooms, it shows us beauty. If it doesn't bloom, it teaches us hope." (from China)
A good addition to fertilizing with compost or manure is various waste that comes together in the kitchen every day:
- Coffee: contains many important nutrients, minerals and trace elements, but acidifies the soil over time. Therefore only use occasionally and not constantly. Dry the coffee grounds well (otherwise they will mold!) and work them into the soil.
- Banana peels: are rich in potassium, so work them into the soil when fertilizing in summer (if possible in a blender).
- Wood ash: is ideal as a rose fertilizer, but only if pure, untreated wood was burned. Wood ash contains a lot of potassium and lime, and the material also inhibits the growth of fungi.
It is important to carefully work the respective raw materials into the soil and then water them. This is the only way the nutrients get to the roots.
Frequently asked questions
Can you also use rose fertilizer for other types of plants, such as clematis?
Of course you can also use rose fertilizer for other types of plants. Many manufacturers explicitly recommend fertilization for other (flowering) shrubs and perennials if they are to bloom profusely. Due to its composition, rose fertilizer is particularly suitable for trees from the rose family, for example wild roses such as the dog rose or apple rose, for crab apples and ornamental quinces as well as for many fruit trees.
The special fertilizer is also well suited for shrubs such as lilacs (Syringa and buddleia), forsythia, laburnum and viburnum. Many gardeners also provide their hydrangeas with it and have had good experiences. The clematis, which is often cultivated together with roses, can also be supplied with rose fertilizer, as can honeysuckle. Rose fertilizer is only unsuitable for plant species where the focus is primarily on the growth of the shoots and leaves (e.g. lawns, green plants and hedge plants). For vegetables, on the other hand, the special fertilizer is dosed too low and is therefore not sufficient.
My roses suddenly have yellow leaves, what's wrong?
Yellow leaves often indicate a care error; there is often a nutrient deficiency behind it - but not always! Sometimes they are the first indication of the onset of sooty mold, a fungal disease that often occurs on roses. However, if the leaves become increasingly lighter while the leaf veins remain dark green, this is an iron deficiency. You can remedy this with a special iron fertilizer, and you should also check the pH value of the soil - if it is too acidic, the shrub cannot absorb enough nutrients through its roots. The same applies if you keep the rose too wet.
My roses don't want to bloom, do they need more fertilizer?
There can also be many reasons for the lack of flowering; inadequate fertilization is not always the cause. So before you resort to fertilizer, first rule out other sources of error. These include: incorrect location (too little light), unsuitable soil (too poor, too acidic, heavily compacted), waterlogging (compacted soil, incorrect watering), diseases and pests and incorrect cutting. When pruning, pay close attention to the recommendations for your rose varieties, otherwise you will accidentally cut off the flower buds and deprive yourself of the flower.
Tip
You can also make a liquid rose fertilizer yourself: To do this, make a plant manure made from nettles and field horsetail, which you add primary rock flour to. Before use, dilute it in a ratio of 1:9 (1 part manure, 9 parts soft water) and water your roses with it every two weeks.