- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-26 14:17.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:19.
Usually you keep your houseplants in normal potting soil, which is composed according to the needs of the respective species. Such plants need to be watered regularly and with great care. Using hydroponics or another water storage system can make plant care much easier.

You don't need a green thumb for plants to grow he althy and beautiful. All you need is the right system and a little attention.
What is hydroponics?
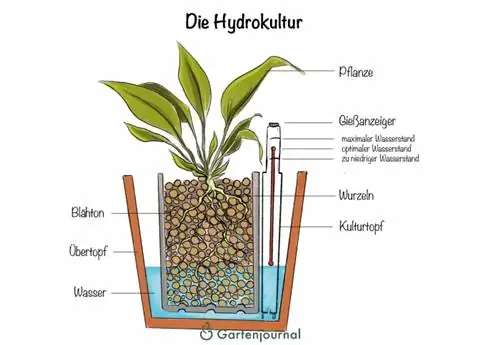
The term “hydroculture” is made up of the two words for “water” (Greek: hydor) and “cultivation” (Latin: cultura), so strictly speaking it means something like “water cultivation”. Hydroponics can therefore be seen as a counterpoint to classic earth culture. After all, plants need nutrients, water and air - but not necessarily soil for all of this, after all, with sufficient nutrition, the substrate only fulfills the function of a root holder. However, the plant also finds support in other materials, such as expanded clay, and therefore gets along wonderfully without conventional potting soil.
What are the advantages of hydroponics?
But why do you cultivate your houseplants without any potting soil? The answer to this question is very simple, because hydroponics offers a whole list of advantages:
- You have to water less.
- You can water your plants precisely because the plant can always get as much as it needs.
- Overwatering or forgetting to water is hardly possible anymore.
- Water requirements are specifically displayed.
- This keeps the plants he althier and lives longer.
- Pests hardly have a chance on he althy plants.
- The substrate can no longer acidify or become muddy.
- Increase the humidity in the room.
A hydro system also makes it easier to care for houseplants during your vacation, because in this case you simply water them in reserve and are no longer dependent on a vacation replacement. This is why hydroponic plants are so practical, especially in offices - everyone can check here when it's time to water.
Background
Hydroculture for allergy sufferers
Another advantage is that mold and earth-dwelling pests such as mourning flies can no longer grow in the clay granules. Hydroponics are therefore also very suitable for allergy sufferers who have always suffered from he alth problems due to soil cultivation and have therefore avoided houseplants.
Which plants are suitable for hydroponics?
While until a few decades ago the selection of plants for hydroponics was quite limited, today almost all species can be cultivated without soil. In addition to the usual green plants, which we present to you in the table below, even orchids and cacti thrive in a soilless culture. The orchids that bloom all year round, such as the uncomplicated Phalaenopsis (also known as the butterfly orchid) or the lady's slipper (Cypripedium calceolus), which is somewhat more delicate to care for, are particularly suitable for this, as these species can be kept warm all year round and do not need a break. Hydroponics is also suitable for tillandsias.
You need to pay attention to these points when caring for orchids in hydroponics:
- Orchids are very sensitive to water.
- Therefore, only fill the water level up to half of the optimum mark.
- If the watering indicator drops to “minimum”, wait two to three days before refilling with water.

Many plants are suitable for hydroponics
These green and flowering plants thrive particularly well in hydroponics:
| Art | Latin name | Origin | Location | Temperature | Care | Special features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree Friend | Philodendron | South America | bright, but avoid direct sunlight | at least 12 to 15 °C | high water requirement | high humidity |
| Begonia | Begonia | Equatorial regions | partially shaded to shady | normal room temperature | water moderately | Continuous bloomers |
| birch fig | Ficus benjamina | India and Nepal | bright, but not exactly sunny | not colder than 15 °C | water moderately, do not use hard water | likes high humidity |
| bow hemp | Sansevieria | Africa | bright | 20 to 25 °C | low water requirement | various types, air purifying |
| Dieffenbachie | Dieffenbachia | South America | bright, but not exactly sunny | at least 15 °C | high water requirement | poisonous |
| Dragon Tree | Dracaena | tropical Africa and Asia | partially shaded to shady | at least 12 to 15 °C | keep dry | various types |
| Single sheet | Spathiphyllum | South America | partially shaded to shady | normal room temperature | water abundantly | air purifying |
| Elephant foot | Beaucarnea recurvata | Mexico | full sun to shady | 18 to 30 °C, cooler in winter | moist, but not waterlogged | Succulent, also called bottle tree |
| Flamingo flower | Anthurium andreanum | South America | bright, not exactly sunny | not cooler than 15 °C | water moderately | very easy to care for |
| Lucky Feather | Zamioculcas zamiifolia | East Africa | bright to partially shaded | normal room temperature | water moderately | very easy to care for |
| Kentia palm | Howea forsteriana | Australia | from sunny to shady | normal room temperature | water moderately | very easy to care for |
| Monstera | Monstera deliciosa | Central and South America | from sunny to shady | normal room temperature | water moderately | air purifying |
| Cycad fern | Cycas revoluta | Southeast Asia | full sunny | normal room temperature | don’t water too much | also known as sago palm |
| Yucca palm | Yucca elephantipes | Central America | partially shaded to shady | at least 15 °C | water little | can tolerate dry indoor air |
| Wonderbush | Croton petra | India | bright to partially shaded | at least 12 to 15 °C | moist, but not waterlogged | also known as croton, poisonous spurge plant |
Caring for cacti in hydroponics
Even cacti thrive in hydroponics as long as you don't fill the water level higher than the optimum mark. After the water level has dropped to “minimum,” wait about three to five days before watering again. During the winter months, many species are no longer watered, but only wetted. You should also rinse the nutrient solution out of the pots during the dormant period. Use a substrate with as large a grain as possible for cactus cultivation.
Excursus
Can you also grow vegetables and lettuce hydroponically?
In fact, growing vegetables, lettuce and herbs in water storage systems is also possible. In industrial agriculture, many areas now only work with a substrate-free culture, in which the plants grow in a nutrient solution enriched with oxygen. This system is also known as “hydroponics” or “hydro-grow” and can also be used on the balcony at home, especially for heavy-feeding and thirsty species such as tomatoes. You can purchase special systems and the corresponding nutrient solutions from specialist retailers.
The following video shows how this can work:

What materials do you need for hydroponics?
However, you cannot use normal flower pots for hydroponics that you simply fill with expanded clay and water. Here the plants would literally suffocate within a very short time because their roots are in the water and therefore no oxygen can reach them. The trick with water storage systems is to separate the substrate and the water supply from each other and only give the plants the opportunity to get the moisture they need themselves. The plant roots are not permanently in the water and receive sufficient air. For hydroponics to work, you need the materials and accessories described in this section.
Planters
Classic hydro systems usually consist of two planters: The culture pot contains the clay granules and the plant, and the water level indicator is also installed here. Many hydro culture pots have a special opening for the water level indicator and others for administering the nutrient solution - the roots also grow from this. In principle, a culture pot is a holding system that is inserted into another vessel - a suitable planter of a suitable size. Culture pots are available in many different sizes.
Water level indicator
The water level indicator is indispensable in hydroponics as it shows the plants' current water requirements. This makes it easy for the indoor gardener because they can see at a glance whether and how much water the plant needs. The aid reacts to changes in the water level and also shows when fertilization needs to be carried out again. The water level indicator is also available in different sizes, which can be selected to match the culture pot.
Planting granules

Expanded clay is used as planting granules for hydroponics
Conventional potting soil is an organic material that is created through decay and decomposition processes from dead plant and animal remains. With hydroponics, however, you use an inorganic substrate that does not contain any lime. There are various options for this, with expanded clay and other clay granules probably being used most frequently. These are clay balls that are available in different strengths. Expanded clay absorbs water like a sponge and also has many air pores so that the roots do not suffer from a lack of oxygen. In addition, this material can be cleaned and reused after each repotting. In addition to expanded clay, these materials can also be used as a substrate:
- gravel
- Sand
- Bas alt
- Mineral wool
Which hydrosubstrate is best depends, among other things, on the specific plant. The grain size of the substrate also depends on the species.
Fertilizer
For hydroponics, a special fertilizer is used that is precisely tailored to the needs of plants cultivated without soil. Normal plant fertilizer is not suitable for this purpose, as the dosage is far too high and over-fertilization would occur within a very short time.
Converting houseplants to hydroponics
Converting houseplants that were previously cultivated in soil to hydroponics is a delicate matter because many plants cannot tolerate this step. Therefore, it is best to purchase hydroponic plants from the outset or to grow self-cut cuttings in expanded clay from the start.
If you want to convert your soil crops to hydroponics, it is best to take this step in spring. At this time, repotting is usually necessary anyway, and the plants now have the best chance of growing. Proceed as follows:
- Lift the plant out of the previous pot.
- Carefully remove any adhering soil from the root ball.
- You can carefully wash the roots with water.
- Then hold the bare-root plant in the culture pot.
- also the water level indicator
- Fill pot with expanded clay
- Carefully tap the pot on the table so that the beads are distributed evenly.
- add granules if necessary
- Place inner pot in a waterproof planter
- Now water the plant up to the “minimum” display.
- Water again as soon as the display falls below “minimum”.
After the change, the plants need a few weeks to grow. It is best to leave the water level indicator at “minimum” or, if you are dealing with thirsty plants, up to “optimum”. Only in exceptional cases, for example when you are away, should the “maximum” be used.
Proper care and repotting of hydroponics

Hydroponic plants also need to be repotted
The subsequent care of hydroponics is straightforward: depending on the type of plant and its nutrient requirements, fertilize it every two to four weeks. To do this, use a special fertilizer for hydroponics, as normal plant fertilizer is dosed too heavily. The water level indicator shows when it is time to water: If this falls below “minimum”, you should top up with water. However, do not use the “maximum” and only water as much as absolutely necessary, otherwise rot can occur. If the roots are permanently in water, this means the death of the houseplant.
Houseplants in soil culture shouldn't necessarily be repotted every year, but they do need a regular substrate replacement - after all, the old soil wears out and has to be replaced with fresh one. This reason is eliminated with hydroponics. Repotting is actually only necessary if the plant has become too big for its container and needs a new one. It might just make sense to remove and replace the top two to four centimeters of expanded clay every year. Over time, these accumulate with nutrient s alts and turn an unsightly white color.
Excursus
Can you also grow cuttings hydroponically?
If the plant to be grown from the cutting is later to thrive in hydroponics anyway, it makes sense to grow the young plant in a soilless substrate right from the start. Cut the desired cuttings and plant them in very fine-grained expanded clay. Now care for the plant like any other cutting: ensure that the air is ventilated by placing a plastic or glass hood over the planter, keep it moist (just moisten the substrate!) and ventilate daily. As soon as the cutting shows its first growth, repot it into coarser substrate. Don't make the mistake of trying to root cuttings in a glass of water first. This often goes wrong.
Alternatives to hydroponics
In addition to the classic form of hydroponics, there are other systems that work with a water reservoir and are also suitable for houseplants.
Planting systems with clay granules
For a pot culture with Seamis, for example, you use clay granules that store water and only release it to the plant roots when needed. When switching from soil to granulate culture, you don't have to wash any remaining soil from the roots, but simply replant the plants together with their pot balls. Fill the remaining space between the root ball and the vessel wall as well as the surface of the earth ball with granules, which is why the waterproof planter has to be about a third larger than actually needed. First fill the bottom of the pot with a layer of granules up to about a third of the total height of the pot.
A moisture meter is also used here, but it has to be inserted into the ball of earth. The tool does not show the water level, but rather the degree of moisture content of the root ball. Water your houseplant as soon as the moisture meter turns red. As a guideline for the amount of water, use about a quarter of the pot's volume. Don't be irritated if the indicator doesn't turn blue immediately after watering: it takes a while. Don't make the mistake of pouring more water than needed.
Earth culture with water reservoir
In addition, houseplants can also be maintained in a soil culture with a water reservoir, although special systems are required for this. Otherwise there would be waterlogging and the subsequent death of the plant in question. Instead, add a partition between the potting soil and the plant roots in it and the bottom of the container. The water reservoir is located below this and keeps the substrate evenly moist, but not wet.
Houseplants cultivated in this way rarely need to be watered. Pour the water through a watering shaft on the edge of the pot and not directly onto the soil!
Frequently asked questions
Does hydroponics actually have disadvantages?
In fact, hydroponics also has disadvantages. These consist primarily in the system's high susceptibility to errors: a single overdose, for example with nutrient solution or even with water, can have devastating consequences and endanger the he alth of the plant. It also makes sense to check the pH value from time to time so that it always remains in the optimal range.
What is the white coating on the substrate?
The whitish coating on the clay granules is mineral deposits and is in no way mold. Clay is an inorganic material and therefore cannot get moldy. Wash the coating under clear, running water and then allow the cleaned granules to dry. Then you can use it again and again.
Is it true that vegetables grown hydroponically don't taste as good as those grown in soil?
Indeed, the taste of hydroponic vegetables and other crops is often criticized. Vegetables and herbs would taste bland because they could only develop little flavor. The uniform taste is one of the disadvantages of such a system.
What do I do with my hydroponic plants when I go on vacation?
In such a case, you can exceptionally fill the water level to “maximum” and go on vacation with peace of mind. Your houseplants will be adequately cared for in the next few weeks.
How do you know that the water level indicator is broken?
The water level indicator can break or become blocked for various reasons, for example because the plant roots grow into the aid. You don't always notice the lack of functionality. However, there are tell-tale signs: If the otherwise fairly consistent watering rhythm suddenly changes (often weekly), then this could be due to a broken water level indicator.
Tip
If the planter you choose is too big for the plant or it is too deep in the water, you can place it on a polystyrene insert and get it out of the danger zone.






