- Author admin leonars@hobbygardeners.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 16:46.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 11:22.
Potato towers come in different versions. Most of them are advertised with the promise of a large harvest with little space. However, due to different characteristics, they produce less or at most the same yield as cultivation in beds, raised beds, tubs and bags.

Does growing in a potato tower work and which varieties are suitable?
A potato tower allows you to grow potatoes in a small space by allowing the plants to grow taller. However, the yields are usually the same or lower than with conventional farming methods. What is important is a maximum tower height of 45-50 cm, double hilling and rope-forming potato varieties such as Agria or Granola.
What is a potato tower?
The potato tower is a relatively new trend for potato cultivation. The basis for orientation is the principle of the raised bed. Planting the nightshade plant generally requires a lot of space. However, not every hobby gardener has enough space available for this endeavor. This is exactly where the potato tower comes in, which promises a high yield on a small footprint.
The basic principle of cultivation is explained quickly and easily. One or more potato tubers are placed in a stable framework made of, for example, wire mesh and straw. As the growth height increases, the inner area is filled with soil and compost. The root strands (stolons) on which more and more new potatoes are formed also increase to the same extent. In theory, an almost infinite number of new daughter tubers can be created in a very limited space.

The classic structure of the potato tower consists of a wire mesh covered with straw. Inside, this is then constantly filled with soil and compost.
Types of potato towers
There are a variety of different variations for building your own potato storm. But not every construction method is suitable for growing potatoes without any problems. Below we will introduce you to six different methods in terms of their structure, functionality and possible problems.

Wire potato tower with a tuber
Construction: A wire mat of any size is formed into a tube using cable ties. This is then attached to the ground and filled up to 1/3 with hay, leaves, compost and soil. The seed potato is then placed in the middle and additionally covered with soil.
How it works: As the potato plant grows, the area around the tuber is steadily piled up. This prevents the formation of the toxic substance solanine in the tuber.
Problem: In theory, the constant piling up of new layers of soil should promote the formation of additional stolons and new potatoes. However, in practice it has been shown that this leads to stress reactions in the plant. In order to continue photosynthesis, the plant must continue to grow higher. In addition, the energy required to supply water and nutrients increases.
Wire potato tower with several tubers
Construction: A wire mat of any size is formed into a tube using cable ties. This is then attached to the ground and filled up to 1/3 with hay, leaves, compost and soil. The seed potatoes are then placed in turn around the edge (5 centimeters apart) and additionally covered with soil.
How it works: As the potato plants grow, the areas around the tubers are steadily piled up. This prevents the formation of the toxic substance solanine in the tuber.
Problem: In theory, the constant piling up of new layers of soil should promote the formation of additional stolons and new potatoes. However, in practice it has been shown that this leads to stress reactions in the plant. Growing several tubers in one container also leads to high competition among each other for irrigation water and minerals.
Wooden potato tower
Construction: The wooden version consists of several wooden boards of the same size and an open floor. To prevent the wood from getting wet, the inside of the potato tower can be lined with pond liner (€10.00 on Amazon). Ideally, all parts are attached to each other with nails or screws. The filling is then carried out according to the previously mentioned scheme. In addition, several boards can be inserted with increasing piles.
How it works: The continuous layering of new soil is intended to stimulate tuber formation.
Problem: In particular, building a potato tower made of wood is significantly more time-consuming than the wire version, but it is more durable. Here, too, the potato plant is put under stress. On the one hand, it has to grow higher and higher to develop new leaves, and on the other hand, it fights for light, water and nutrients with several other planted tubers.
Potato tower with door
Construction: The potato tower with door is constructed in the same way as the wooden version. Before filling, a hole of the desired size is cut out. This cutout can then be attached to the actual construction using hinges. It's supposed to make harvesting easier. To prevent the wood from getting wet, the inside of the potato tower is lined with pond liner (€10.00 on Amazon). The filling is then carried out according to the previously mentioned scheme.
How it works: The constant layering of new soil is intended to stimulate tuber formation, but puts the plant under stress.
Problem: In particular, building a potato tower made of wood is significantly more time-consuming than the wire version, but it is also more durable. If only one tuber is planted, the tower can function like a plant pot up to a maximum height of half a meter. If there are several tubers there is competition and the harvest is smaller.
Potato tower with car tires
Construction: In this case, car tires that are stacked on top of each other serve as a framework for the potato tower. Typically between two and three are used. The inside is then filled again with hay, leaves, compost and soil.
How it works: The seed potatoes are planted inside the tires and continually piled up with substrate. This promotes the growth of the above-ground area as the plant must continue to photosynthesize for the development of the tubers.
Problem: The use of car tires as a barrier poses the risk of the accumulation of various harmful substances. These include butadiene, which is considered to cause cancer, and thiuram, which is known to be a common allergy trigger. With this variant, too, the altitude is a stress factor that can reduce the harvest.
Does a potato tower work?
The success of a potato tower can only be assessed in comparison to other cultivation methods. If it generates higher yields in relation to an alternative planting in the bed or another container, it is considered successful and functional. A potato tower usually works just as well or worse than planting in a bed. This is due to the structure and height.
Building a potato plant
The origin of a potato plant lies in a potato tuber. During germination, a stem sprouts from this, on which flowers later develop. Roots form underground on the mother tuber and serve to absorb nutrients and water. In addition, horizontal supporting threads, the stolons, grow from the underground part of the stem. Over time, these are the only areas where the new potatoes develop.
Both the section in which the potato plant forms stolons and the number of potatoes growing per supporting thread are limited depending on the variety. For this reason, not all varieties are suitable for tower planting.
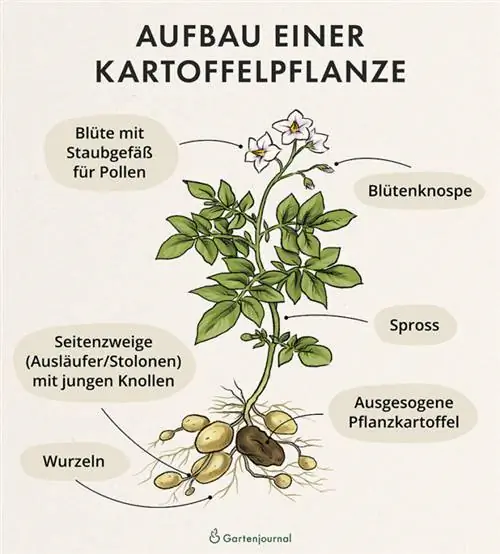
Tump formation in potatoes
The arrangement of newly formed potato tubers varies depending on the variety. Basically, you can distinguish between three different growth forms (source: News from the Landei):
- Plateau
- Ball
- strand
The ideal shape for forming new tubers in a potato tower is the rope shape. Up to a certain height, this forms more stolons where potatoes form. Plateau-shaped and spherical potato varieties are better suited for sack or pot planting because they grow widthwise rather than height. This is due to the breeding for agriculture, because the common potato varieties for private gardens are also grown in industry. A wider growth is more efficient for the harvest than a deeper growth. With a few exceptions, the deep growth does not correspond to the normal growth of the potato.

The following varieties can be assigned to the growth forms:
Plateau growth:
Bamberger croissants
Ball growth:
- Agria
- Belana
- Blue Congo
- Bölzig's Yellow Flowering
- Kennebec
- Melody
- Negra
Strand Growth:
- Agricultural blessing
- Danish asparagus potato
- Eerstling
- Granola
- La Ratte D`Ardèche
- Violette D`Auvergne
- Vitelotte Noire
You can find more information on Nadja’s YouTube channel at “News from the Country Egg”. In the following video, Nadja goes into more detail about her experiment of growing potatoes in a sack and shares her experiences and tips.

Growth in the potato tower
The ideal potato tower allows growth to almost infinite heights. This growth ensures a rich potato harvest with as little space as possible. However, this ideal cannot be confirmed in practice, as some natural conditions represent an obstacle.
Major problems are:
- Training of stolons and potatoes is limited
- Constant piling up of soil makes it difficult to supply the areas below
- mainly lower layers are at risk of drying out
- Growing multiple tubers leads to competition for water, nutrients and space
- Weight of the soil leads to the formation of smaller potatoes
- Openings on the edge offer a high evaporation area

Summary
Basically there is nothing wrong with growing potatoes in a potato tower. However, the enormous harvest yields mentioned in many articles will be at a significantly lower level in practice. The ideal potato tower therefore only exists in theory. Nevertheless, this form of cultivation can certainly achieve a sufficient harvest yield if certain general conditions are adhered to.
Growing in a bucket or sack is significantly less labor-intensive to maintain and just as space-saving. Further information on this can be found in the next section. If you still value a potato tower, please note the following information:
- maximum one potato tuber per tower
- Tower height of a maximum of 45 to 50 centimeters (sources: cultivariable, a piece of rainbow)
- hilling twice until flowering is sufficient
Potato towers can work best if you treat them like plant pots. (Source: a piece of rainbow)

When choosing which variety to plant, you should primarily use ball-forming or strand-forming species. The types Agria, Kennebec, Ackersegen and Granola are particularly popular. For all other genres, we recommend doing your own experiments and testing.
Alternative to the potato tower
An alternative to growing potatoes when space is limited is the bucket. As with planting in beds, planting takes place between the beginning of April and the end of May. While late potatoes should be planted earlier due to their long ripening period of up to 160 days, early potatoes, which require between 90 and 140 days, can also be planted later. After the Ice Saints at the end of May at the latest, there is no longer any danger of late frosts. You can find additional tips for optimal planting of potatoes here.
It's best to avoid using a coaster to avoid waterlogging. If you still don't want to do without it, it is necessary to regularly remove excess water. In general, it is recommended not to plant more than one tuber per bucket. Due to the limited space, there is otherwise a risk of poor development of all plants.
FAQ
How to care for a potato tower?
Caring for a potato tower follows the same standards as planting a bed. The potato plants should be watered and fertilized evenly. As it grows in height, soil should also be regularly piled up on the plant until it blooms.
What types of potato towers are there?
The bottom layer should consist of leaves and branches to create an air-permeable base. This is followed by layers of soil and compost. Leaves and sand can be added as needed to loosen it up. The area with the inserted tuber is also provided with a starter fertilizer such as horn shavings or sheep's wool pellets.
Does a potato tower work?
Potato towers come in a variety of designs. The most well-known shapes are made of wire, wood (possibly with a door), car tires and plastic.
Does a potato tower work?
The assessment of whether a potato tower works can only be done based on the harvest yield. Compared to alternative cultivation methods in closed systems such as a planter or a bag, higher yields are not achieved. Depending on the variety, reduced yields can even be expected.
How to build a potato tower?
You can make a potato tower yourself or purchase it as a kit. The simplest version is made from a rolled up wire mat that is secured using cable ties.
What is a potato tower?
A potato tower is a planter with a vertically oriented structure. The outer border ensures the stability of the construct and limits the space required. This form of cultivation is primarily used for tall crops such as potatoes.






